
Medication Admin Simulation (Guide + Training Scenarios)
Administering medication is one of the most error-prone and high-risk tasks in healthcare. Textbook learning is often not enough to prepare trainees for the pressure of dosing and timing. Practicing directly on patients, on the other hand, leaves no room for mistakes.
Medication administration simulation bridges this gap by letting nurses rehearse real-world scenarios in a safe, controlled environment.
This article will walk you through what medication administration simulation is, why it matters, common training scenarios, and key safe handling practices.
What Is Medication Administration Simulation?
Medication administration simulation is a training method that recreates the process of giving medications in a realistic but controlled environment.
Learners go through the steps of a “med pass” (medication round) with simulated patients, manikins, or VR, following the same procedures they would in a hospital or clinic. It partially substitutes for real experiences and allows repetition of scenarios without jeopardizing patient safety.
During a simulation, instructors can present realistic challenges (like a sudden change in patient vitals or condition). They then guide learners through the appropriate response.
At Lumeto, we bring this to life with immersive VR training that lets students practice medication preparation, delivery, and monitoring in customizable scenarios.
Here’s a video that shows a Lumeto student practicing medication administration in VR:
Example of a Medication Administration Simulation for Nurses
A typical medication administration simulation might involve a nursing student preparing to give an IV antibiotic to a patient with pneumonia.
The student reviews the eMAR and confirms the “five rights.” They gather and label supplies, then explain the medication to the patient before starting the infusion.
During the scenario, they may face challenges such as a patient refusing the drug, an equipment alarm, or an allergic reaction. Each is designed to test their ability to stay calm, think critically, and act safely.
Benefits of Nursing Medication Administration Simulation
Simulation-based medication training offers numerous benefits for students and practicing nurses:
Improved Patient Safety
Research shows that nursing medication administration simulation can reduce actual medication errors. One hospital initiative found that after nurses underwent targeted simulation exercises, their adherence to medication administration best practices (the safety checks and procedures) jumped from 51% to 84%.
By practicing in a controlled setting, nurses are less likely to make those mistakes on real patients. In fact, simulation has become a key component of patient safety training, as it enables clinicians to identify and correct errors before they occur in real patients.
The ultimate goal is fewer adverse drug events, which currently account for an estimated 700,000 emergency visits and 100,000 hospitalizations each year.
Increased Confidence and Competence
Repeated practice in simulations helps build muscle memory and confidence in medication skills. Nursing educators note that unlimited practice in a safe setting allows students to master essential skills and feel fully prepared for clinical rotations.
Students can train on tasks such as:
- Calculating medication doses
- Programming IV pumps
- Drawing up injections
- Scanning medication barcodes
- Verifying patient identity
- Setting infusion rates
- Responding to allergic reactions or side effects
- Documenting medication administration
- Handling high-alert medications
- Managing interruptions during a med pass
Learners who start with low-fidelity practice (e.g., injection manikins) and progress to high-fidelity scenarios report feeling much more confident in their ability to give meds correctly.
Toronto Metropolitan University alumna Halyna Yurkiv, in collaboration with Lumeto, proved the impact of immersive VR. In her study, students faced a virtual patient in respiratory distress, complete with alarm beeps, monitors, and life-saving tools. It resulted in significant gains in knowledge, confidence, and preparedness for real emergencies.
Here’s a video of nursing students using Lumeto to assess and treat virtual patients in an interactive hospital setting:
Enhanced Communication
Beyond technical skills, medication administration simulation incorporates teamwork and communication elements. For example, using standardized patient actors or VR patients, learners must explain medications to a “patient” and handle their questions or refusal.
High-pressure scenarios train students to think on their feet and work with the healthcare team. This may include calling a rapid response or notifying the provider.
One study found that simulation training shaped nursing students’ attitudes to be more willing to report and address medication errors, creating a culture of safety rather than fear or blame.
At Lumeto, immersive modules also extend to team-based scenarios like Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support (ACLS). These sessions build both communication and collaboration skills under pressure.
Here’s a video showing how Lumeto delivers ACLS training in VR:
Personalized Feedback
During simulations, instructors closely observe or even record the session. Learners then receive detailed feedback in a debriefing – what they did well and what needs improvement.
For example, if a student forgets to check the patient’s allergy band, the debrief will highlight that omission so they remember it next time. Over time, both learners and faculty can see measurable improvement in skills.
With Lumeto, this feedback goes a step further. As shown in the screenshots above, learners receive a clear breakdown of safe practices completed correctly as well as missed or unsafe practices. Students see exactly where they fell short and focus their practice on those areas.
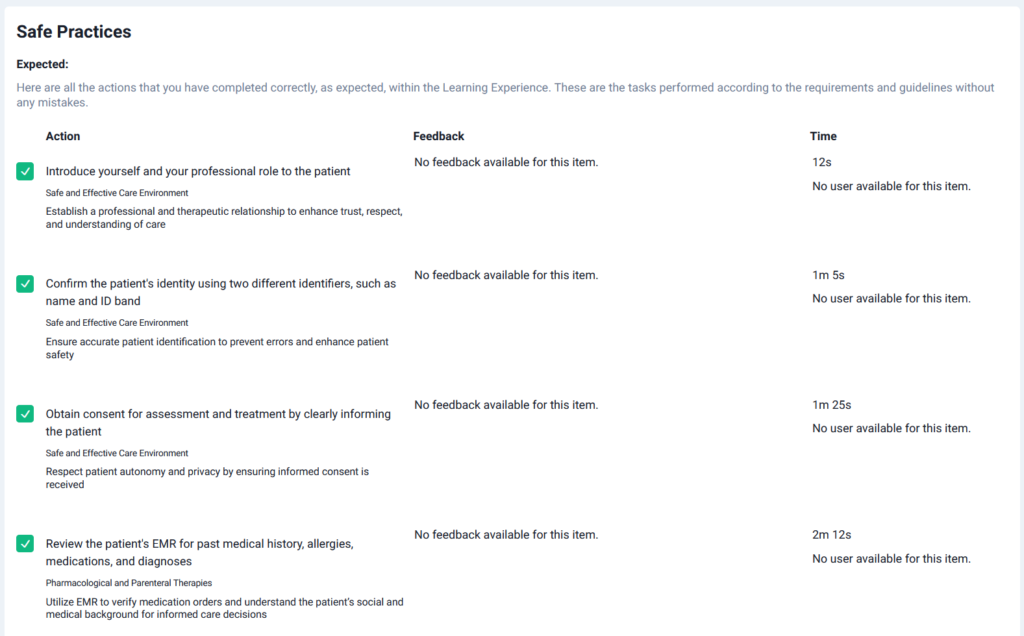
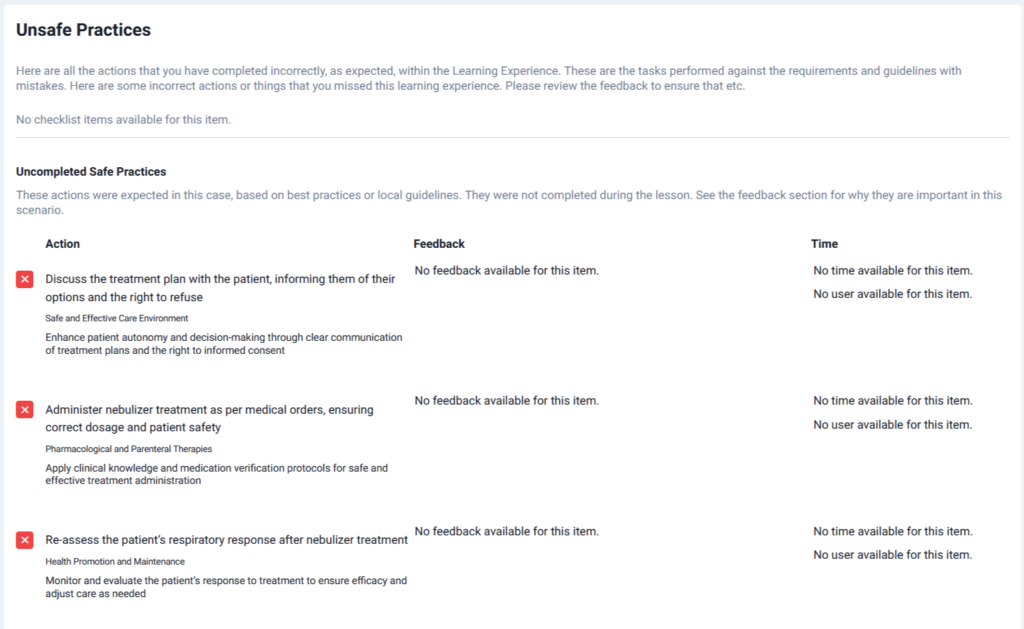
Common Medication Administration Simulation Scenarios
Healthcare training programs in the U.S. and Canada frequently use a set of recurring scenario types to cover the most important aspects of medication safety. Some common medication administration simulation scenarios include:
Managing Adverse Reactions
Scenarios where a patient experiences a negative reaction to a medication are very common. For instance, a simulation may involve a patient developing anaphylaxis or another allergic reaction after receiving an antibiotic.
Other variations include a patient becoming oversedated from pain medication (requiring reversal with an antagonist), or a drop in blood pressure after an antihypertensive dose. These scenarios teach the nurse to recognize side effects and respond appropriately under pressure.
Here’s an example scenario on Lumeto:
Medication Refusal or Mix-up
Simulations often address communication challenges, such as a patient refusing or questioning medications. One classic scenario is a patient with dementia who believes the nurse is trying to poison them. Another is a client who insists, “I’ve never seen this pill before, it’s not what I take at home.”
In these cases, the nurse must verify the medication, reassure or educate the patient, and follow policy. This may include holding the medication if appropriate or convincing the patient to proceed.
Another common scenario involves two patients with the same last name on a unit. Simulations teach nurses to prevent “wrong patient” errors by always using two identifiers.
Here’s a video from Lumeto where a virtual patient refuses to engage with their medical provider.
The student must find ways to build trust, explain the treatment, and move the conversation forward. What makes this powerful is that the scenario is powered by generative AI, so the patient’s responses are created on the spot.
Interrupted Nurse
Interruptions are one of the leading causes of medication errors in real-world practice. A highly realistic scenario type focuses on simulating the distractions that nurses often face during medication rounds.
The simulation’s goal is to teach strategies like stopping and resuming the medication process methodically, or using checklists to avoid losing one’s place.
In a “Nurse Interrupted” simulation, a nurse may be preparing or administering medication when multiple distractions occur at once. For example, an attendant tries to console a pediatric patient in a simulation while the child is crying loudly. At the same time, another staff member might ask a quick question, pulling the nurse’s focus away.
Here’s an example of how this type of simulation looks in action:
High-Risk Medication Protocols
Some simulations focus on high-alert medications that carry greater risk of harm (such as insulin, heparin, chemotherapy agents).
These scenarios drill the extra safety steps required to protect patients and reduce errors.
Key protocols often practiced in simulation include:
- Performing an independent double-check with another nurse before administration
- Following the five rights of medication (right patient, drug, dose, route, time) with extra vigilance
- Verifying medication orders against lab values or protocols
- Calculating weight-based or titrated doses with precision
- Documenting administration immediately and accurately
- Monitoring the patient closely for side effects or rapid physiological changes
- Using proper handling and disposal techniques for hazardous drugs (e.g., chemotherapy)
Lumeto strengthens this process with its assessment dashboard, which tracks every step against safety checklists. Learners see exactly which actions they performed correctly and where they missed a step. This measurable feedback builds respect for high-risk medications while ensuring safer real-world practice.
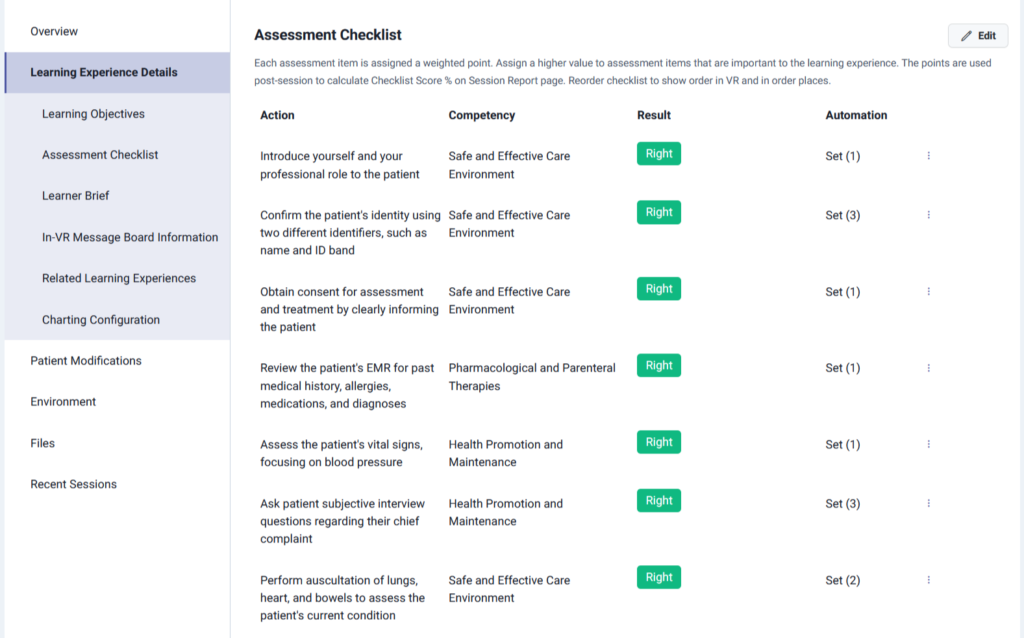
Dosage Verification
Another common scenario is a math-focused med administration drill. For example, students might be given a physician’s order that requires calculation of a dose (such as mg per kg for a pediatric patient, or converting between units).
They then must draw up or program the correct dose on a syringe or IV pump. The simulation might include a subtle twist like an unusual concentration on the vial (forcing them to calculate carefully) or a time pressure element to simulate an urgent situation.
Some nursing schools even incorporate “escape room” simulations where solving dosage calculations correctly is part of the challenge to “escape.”
Best Practices for Safe Handling of Medication Training
There are several best practices that clinical educators follow to maximize learning and ensure safety habits are reinforced:
Emphasize the “Five Rights”
Every training begins with the foundational Five Rights of Medication Administration:
- Right patient
- Right medication
- Right dose
- Right route
- Right time
Simulation exercises should require learners to practice all these checks consistently for every medication given.
The World Health Organization stresses that preventing medication errors “requires putting systems and procedures in place to ensure the right patient receives the right medication at the right dose via the right route at the right time.”
Many institutions have expanded this list to include additional rights such as right documentation, right reason, right response, right to refuse, and right education.
Start Simple
Best practice is to start novice learners with a standardized, simple scenario and then add complexity as they advance.
Initially, simulations might involve one patient and one or two medications, allowing the student to go step-by-step without too many curveballs. They follow a standard routine until they’re comfortable. As competence grows, educators can introduce more realistic challenges.
For instance, an advanced scenario might intentionally remove the patient’s ID wristband to see if the nurse realizes and finds an alternative way to identify them. Or the instructor might “bury” an allergy in the patient’s history and include that allergen in the med list, testing if the student checks for allergies.
On platforms like Lumeto, these adjustments are easy to set up. In the screenshot below, you can see how a trainer can quickly edit a patient profile, adding a known allergy, changing medications, or modifying medical history.
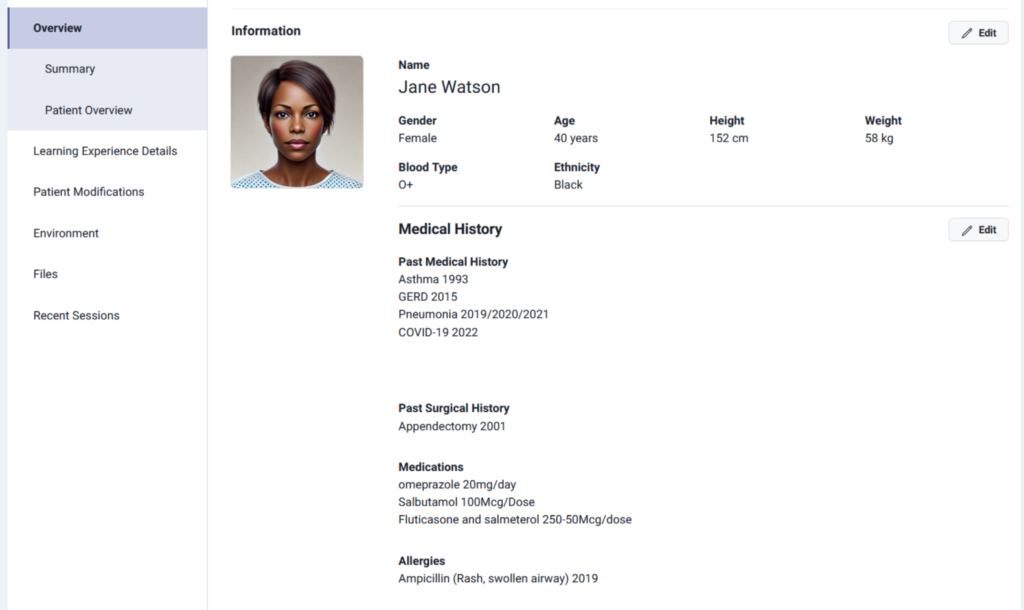
Regular Refreshers
For safe medication handling, one-and-done training isn’t enough. Best practice is to provide regular simulation refreshers or competency assessments.
Hospitals in North America increasingly use simulation in annual staff education or when introducing new medication policies/equipment.
With Lumeto’s Artificial Clinical Evaluator (ACE), performance feedback is tracked over time so staff can see improvement and remain accountable.

Use Realistic Tools and Environment
The more closely the simulation setup resembles the real clinical environment, the more effective the training. Best practice is to use the actual medication administration tools that nurses use on the job.
VR is one of the best ways to achieve this realism. Instead of a static classroom setup, students work in a fully interactive hospital environment where they can administer medications using lifelike equipment.
With Lumeto, learners gain access to customizable virtual environments stocked with realistic tools, from infusion pumps to medication carts.
For example, in Lumeto, a stroke patient assessment can be simulated, allowing students to evaluate symptoms, check vital signs, and initiate the right protocols, all inside VR. It ensures learners are ready to respond quickly and accurately when facing the same situation with real patients.
How Lumeto Helps With Medication Administration Training
Lumeto is a cutting-edge VR simulation platform that puts many of the best practices described above into action. Our InvolveXR approach removes common barriers found in traditional simulation labs. These include limited space or equipment, and the need for all learners to be physically on-site.
With InvolveXR, students can join from different campuses or even from home and still train together in a shared virtual environment.
The platform supports both:
- Synchronous group training (where an instructor leads a class in the same scenario, and students take turns administering medications).
- Asynchronous practice (where learners can repeat scenarios on their own time).
It allows students to get more hands-on practice without being restricted by lab schedules.
Another unique strength of Lumeto is its AI-powered patients. These virtual patients don’t just follow scripts; they respond emotionally and behaviorally.
A patient might act anxious, confused, or even resistant, forcing students to adjust their communication in real time. This adds a critical interpersonal layer to medication administration training, preparing future nurses not only to give medications safely but also to communicate effectively with the patients in their care.
Here’s an example of a frustrated AI patient:
See how Lumeto can support your medication administration training. Book a demo today!
Frequently Asked Questions
Is medication administration simulation used to prepare nurses for licensure exams?
Yes. Nursing programs align medication administration simulations with NCLEX-style competencies. Practicing these scenarios helps students master both the technical steps and the critical thinking skills they’ll be tested on.
How do educators measure success in a medication administration simulation?
Success is measured by completing the med pass and by consistency in following protocols, managing stressors, and communicating effectively. VR training platforms provide dashboards and analytics so faculty can track performance over time.
How does simulation help with interprofessional education?
Medication administration simulation can involve pharmacy, medical, or respiratory therapy students to practice team-based communication during complex med passes.