
Medical Simulation Equipment: Types, Uses, and Benefits
Medical simulation equipment is used in nearly every healthcare training facility. However, the cost and infrastructure requirements can significantly influence the choice of equipment.
Is it better to invest in advanced virtual reality simulations that offer immersive experiences? Or should institutions stick with tried-and-true methods like task trainers and manikins?
In this article, we’ll explore the types of medical simulation equipment, their uses, and the benefits they provide.
What Is Medical Simulation Equipment?
Medical simulation equipment is the range of tools used to recreate clinical scenarios for training healthcare professionals. These can include manikins, task trainers, and virtual and augmented reality systems.
Modern simulation tools have become integral to medical education and the patient safety movement. Medical simulation training equipment allows learners to practice high-risk procedures and decision-making in a safe, controlled setting.
High‑fidelity simulation allows up to 50% of clinical training hours to be replaced in nursing education without compromising quality.
The choice of equipment depends on the learning objectives and available resources. As of 2025, the global medical simulation equipment market is estimated at US $962 million, with a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 4.3%.
Notably, Lumeto’s InvolveXR platform is a prime example of advanced simulation technology: it provides an immersive training environment that institutions can use to train and assess healthcare staff across locations in a consistent way.
Common Types of Medical Training Equipment
Some common types of medical simulation equipment include:
Medical Manikins for Training
Medical manikins (or mannequins) are full-body patient simulators designed to look and respond like human patients. They are made up of basic plastic dummies or high-fidelity electronic models. They can mimic many human functions, such as breathing, bleeding, displaying vital signs, and even speaking.
Almost all healthcare providers use manikins during Basic Life Support (BLS) training.
A single advanced patient simulator can cost anywhere from $10,000 up to $85,000 or more, depending on features. Top-of-the-line models offer extremely lifelike responses but require significant investment and upkeep.
Task Trainers
Task trainers are focused simulation tools that represent a specific body part or system for practicing a single clinical skill or procedure.
Modern task trainers allow repeated, targeted practice of skills until proficiency is achieved. A student might, for example, insert dozens of IVs into a silicon arm or perform injections on a padded surrogate skin.
They are often more affordable than full manikins. A basic CPR torso or IV arm may cost only a few hundred dollars.
Examples include:
- Arm model for IV insertion
- Airway head for intubation practice
- Pelvic model for obstetric exams
- Thoracentesis trainer for chest tube placement
Virtual Reality (VR) Simulation Systems
VR simulation systems place learners in a computer-generated healthcare setting. Trainees wear a VR headset (and often hand controllers or gloves), and they find themselves in a realistic 3D environment. It could be an operating room, emergency department, or any setting programmed into the software.
A key benefit of VR is that it enables multi-user training even when participants are in different physical locations. VR also offers unlimited repeatability, and parameters can be changed easily (unlike with physical setups).
VR simulation has advanced rapidly. Today’s systems feature lifelike graphics and physics. Some also incorporate voice recognition or AI-driven patient behavior.
Lumeto is at the forefront of VR simulation in healthcare. We use artificial intelligence to enhance the training experience. Instructors can customize virtual patients and scenarios (for example, changing the patient’s history, vital signs, or behavior) to meet specific learning objectives.
Lumeto offers a screen-based mode not requiring a headset, which makes high-quality simulation accessible in classrooms, offices, or at home.

Haptic Feedback Devices
Haptic feedback devices add the sense of touch to simulation training. They provide tactile sensations ( such as resistance, vibration, or pressure) to simulate what a procedure feels like.
For instance, a surgical simulator might have haptic-enabled instruments so that when a learner “cuts” or sutures tissue in a virtual environment, they feel realistic resistance.
Studies have found that adding haptic feedback can improve skill training by reinforcing muscle memory and tactile decision-making. Haptic VR is also able to induce stress levels in trainees comparable to those in real life.
Full Simulation Labs
Simulation labs (sim labs) replicate real clinical environments for training purposes. They contain multiple rooms staged as hospital units, such as an ICU room with a hospital bed and other equipment. These labs often include high-fidelity clinical simulation equipment to mimic real-world care environments.
Sim labs are typically equipped with:
- Audio-visual systems to record scenarios
- Control rooms with one-way mirrors for instructors to observe
- Debriefing rooms where participants review a video of their performance.
However, creating and maintaining a simulation lab is resource-intensive. Institutions must allocate significant space and budget to build out these clinical replicas. Even simpler labs require dedicated rooms that not all organizations have readily available.
For organizations that lack the space or funds to build a full mock ward, Lumeto offers a “virtual simulation lab.” Learners can be placed in a realistic virtual hospital environment that mimics those clinical spaces. Here’s an example:
Mixed Reality Tools
Mixed Reality often refers to a spectrum between AR and VR, where virtual objects can interact with the real environment.
AR/MR is beneficial for visualizing things that are normally invisible. One practical application is using an AR app to project anatomy onto a mannequin or standardized patient. For instance, showing the underlying skeletal or organ structures on a live person for anatomy learning.
While still a developing field, early studies and pilot programs suggest AR can improve learning engagement and offer flexibility in simulation.
Uses of Medical Training and Simulation Equipment
Medical training and simulation equipment helps educators teach both technical procedures and critical thinking across a range of clinical scenarios.
Clinical Skills Development
Simulation allows repeated practice and deliberate rehearsal of clinical skills. Studies have shown that simulation-based training improves skill acquisition and retention compared to traditional learning methods.
The immediate feedback and ability to correct mistakes on the spot solidify the learning.
For example, Lumeto developed a difficult airway management scenario in collaboration with the American College of Chest Physicians. In a study, trainees who completed a 25-minute VR session showed a 16% increase in procedural knowledge of airway management, with even greater gains (26% improvement) among resident physicians.

Team-Based Training and Communication
Healthcare is fundamentally a team endeavor, and communication breakdowns can lead to serious errors. Simulation equipment is widely used to train teams to work together effectively.
One prospective study observed that simulation training improves collaborative learning. It also leads to better interdisciplinary communication in emergency department teams.
Team simulations can involve both technical tasks and crucial “soft” skills. Trainees will learn active listening, closed-loop communication (repeating back orders), and briefing or debriefing habits. After the session, trainees can discuss what went well or what could be improved in the team’s functioning.
Lumeto’s multi-user VR capability makes it a powerful tool for team-based training, even when participants are not in the same physical space.
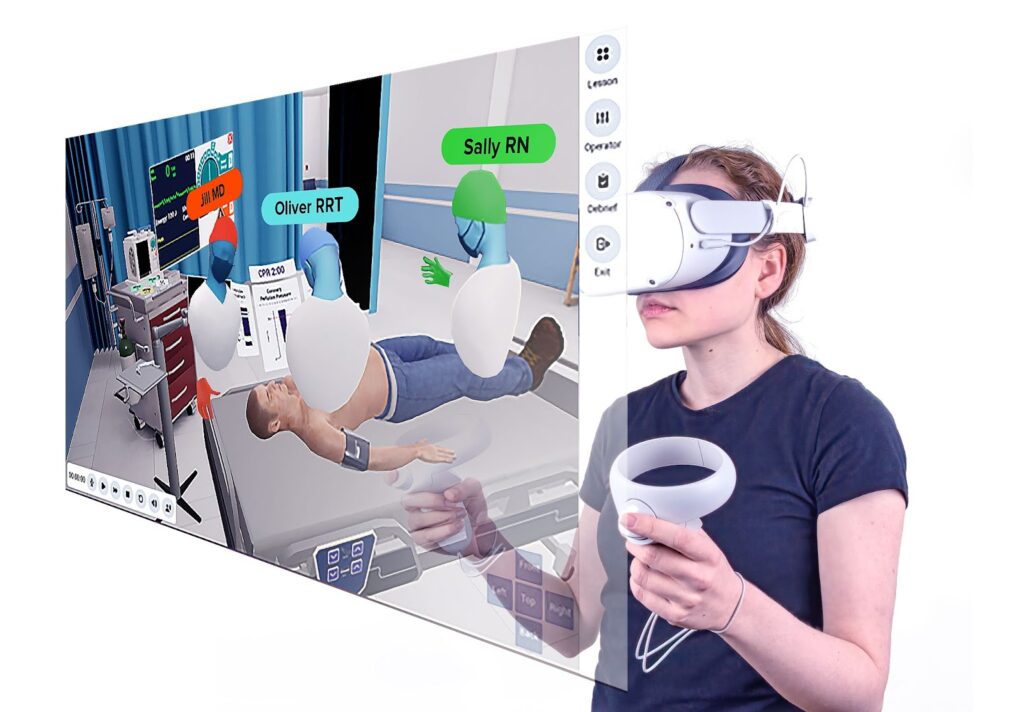
For example, one learner acts as the primary physician, another as a nurse, another as a respiratory therapist. They must communicate via voice and interact within the scenario to care for the virtual patient. This mimics the real-time interplay of a clinical team, as shown below:
Diagnostic Reasoning
Simulation equipment can be used to train and evaluate diagnostic reasoning. They can give exposure to a broad variety of cases, including rare conditions that a student might never encounter during rotations.
This can be done with VR patients or high-fidelity simulations that unfold in real time as learners ask for history, exam findings, or lab results. The goal is to teach how to think through a case methodically and avoid cognitive errors.
Some advanced simulations even measure diagnostic thinking process metrics such as:
- The sequence and relevance of questions asked during the assessment
- Time taken to reach a diagnosis
- Number of diagnostic hypotheses generated
- Accuracy of initial vs final diagnosis
- Use of clinical guidelines or protocols during decision-making
Many Lumeto scenarios begin just like a patient encounter. The learner might enter an emergency room and be presented with a patient who has a set of symptoms. The learner must then assess the patient, order appropriate tests, interpret results, and make a diagnosis and treatment plan.
Here’s how trainees interact with patients on Lumeto:
Medical Error Prevention
There is growing evidence that simulation training reduces errors and improves patient outcomes in real life. One study showed that after nurses underwent targeted simulation training on medication administration safety, their adherence to best practices enhanced from 51% to 84%.
These “simulated errors” become powerful teaching moments. Additionally, simulation is used to train error disclosure and management.
Competency Assessment
Simulation equipment is used to evaluate whether a learner has the required skills and decision-making ability. Many medical and nursing programs employ Objective Structured Clinical Examinations (OSCEs).
Simulation-based assessments can cover technical skills as well as communication. The advantage is that every student or provider is evaluated with the same standardized scenario.
Beyond initial training, simulation is used for ongoing competency checks as well. Hospitals might require practitioners to demonstrate competency in infrequently used skills periodically.
Lumeto’s platform is very well-suited for competency assessments. It can present standardized scenarios to any number of learners and automatically record detailed performance data.
With Lumeto, an instructor can assign a scenario to all 100 students in a cohort. Each student logs in individually and goes through the scenario, which unfolds identically in key aspects. The system can score their actions, as shown in the example below:
Benefits of Medical Simulation Training Equipment
The use of simulation training equipment in healthcare education offers numerous benefits, such as:
Safe Learning Environment
Medical simulation equipment provides a safe environment to learn – “safe” in two senses:
- Safe for patients (no actual patients are at risk during training)
- Psychologically safe for learners (mistakes can be made without catastrophic consequences)
Students can attempt procedures or clinical decision-making that they have never done before. If they make an error, the only “casualty” is a manikin or a virtual patient.
Enhanced Confidence and Readiness
A confident practitioner is more likely to take correct action. And simulation training has a well-documented positive effect on learners’ confidence. Simulation also reduces the anxiety around performing in high-stakes situations.
When students first step into clinics, one of the biggest hurdles is moving from knowing theory to actually doing things for real patients.
Simulation helps bridge that gap by letting them “get their hands dirty” in a practice setting. As a result, they feel more confident to make decisions independently.
Lumeto’s immersive training platform is a confidence booster by design. It allows learners to experience clinical situations firsthand (even if virtual), and it removes much of the fear of the unknown.
For instance, a medical student who has performed CPR on a virtual patient successfully in Lumeto will gain the belief, “If I handled it in sim, I can handle it in reality.” In the Lumeto CHEST difficult airway study, despite 56% of learners having never tried VR before, 73% found that role-playing intubation scenarios in VR was easy to do.

Better Patient Outcomes
Medical simulation training equipment has been linked to improvements in patient care outcomes according to several studies. Not only do simulation-trained practitioners know and do more, but their patients also benefit in measurable ways.
For example, pediatric simulation training has been associated with reduced mortality rates in pediatric emergencies.
For patients, the benefit of being treated by someone who has, say, run through 10 cardiac arrest simulations is intangible but very real. That clinician will be faster and more precise. It will all make a difference between life and death.
Lumeto gives medical trainees the ability to practice critical scenarios like CPR as many times as needed. With real-time performance feedback, learners can instantly see how well they’re performing. Here’s an example:
Standardized Training Across Locations
Traditionally, clinical training can vary widely. Two students at different hospitals might see very different cases. Or two instructors might teach the same skill in slightly different ways.
Simulation offers a way to level the playing field by delivering the same scenarios and assessment criteria to everyone. This is particularly valuable for large institutions such as multi-site nursing programs or in different regions.
It also makes rolling out new training initiatives far more efficient. Instead of sending instructors for workshops or printing manuals, an organization can upload a new scenario to VR training software like Lumeto. All training sites can then begin using it within days.
How Lumeto Helps Deliver Simulation Training
Many educators want to offer more high-quality, hands-on practice—but physical resources can only stretch so far.
Transitioning training to Lumeto’s VR platform can significantly reduce the maintenance load associated with simulation. With Lumeto, there are no full-body mechanical manikins to service – the “patients” are virtual.
Moreover, because Lumeto reduces reliance on consumables (like you’re not constantly buying replacement veins, fake drugs, etc. for scenarios).
You can track learner performance automatically, customize scenarios to your curriculum, and standardize training across multiple sites, all without increasing faculty workload.
Want to offer consistent, scalable training across your sites without expanding your sim lab? See how Lumeto makes that possible. Book a demo today.
FAQs About Healthcare Simulation Devices
How much does simulation equipment cost?
Medical simulation equipment costs vary widely. Basic task trainers may cost a few hundred dollars, while high-fidelity manikins can exceed $100,000. Virtual options tend to have lower setup and maintenance costs.
How is the effectiveness of healthcare simulation devices measured?
Outcomes are typically measured through skills assessments, scenario performance, and post-simulation evaluations. Some programs also track changes in clinical behavior or error rates.
What are the challenges in setting up medical simulation equipment?
Budget limitations, space constraints, faculty training, and equipment maintenance are frequent hurdles, especially for smaller institutions.
What types of learners benefit from clinical simulation equipment?
Students, residents, and experienced clinicians all use simulation, whether to learn new procedures, rehearse rare events, or maintain team readiness.