
11 Top VR Training Benefits for Skill Development
The global immersive training market is on a sharp upward curve. It’s expected to grow more than four times its 2024 size by 2030.
Virtual reality training is becoming one of the most effective ways to train and develop real-world competencies. It has quickly moved from a novelty to a mainstream training tool, with over a quarter of businesses already using VR/AR for employee training as of 2020.
Yet, many still question whether it’s worth the investment or if traditional classroom or e-learning methods can still do the job.
At Lumeto, we’ve seen these benefits firsthand in healthcare training. Medical students and residents using our VR platform gain hands-on practice faster and with greater confidence.
This article highlights key VR training benefits for skill development. We will explain why more industries are investing in it to reshape professional education worldwide.
1. Improved Knowledge Retention
The immersive, engaging nature of VR helps information “stick” better than passive learning. Instead of passively reading or watching, trainees perform tasks inside an immersive environment that engages multiple senses and reinforces memory through repetition.
A PwC analysis found that VR-based learners retained about 75% of the material taught—far higher than the 5–10% retention typically seen in classroom or e-learning sessions. The difference comes from hands-on engagement and emotional involvement, which strengthen long-term recall.
In healthcare, results are even clearer. CHEST, in collaboration with Lumeto, ran studies across three leading academic institutions. A single 25-minute VR session on difficult airway management produced a 26% relative increase in procedural knowledge among medical residents.

2. Safe Environment for Risk-Free Practice
VR provides a safe sandbox for learning through trial and error. If something goes wrong in the simulation, no real harm is done. Instead, the system might prompt to display the error, and the trainee learns from it.
This is especially valuable in industries where errors can lead to injury, equipment damage, or financial loss. Scenarios can be reset and repeated as many times as needed until mastery is achieved. Here are some industry examples:
- Aviation: Pilots train for conditions too dangerous to replicate in real flights. This may include engine failures, weather turbulence, and emergency landings.
- Manufacturing: Workers learn to operate heavy machinery or handle hazardous materials in a safe digital environment, reducing workplace accidents during training.
Energy and Utilities: Technicians practice responding to electrical faults, oil leaks, or confined-space emergencies in realistic VR setups without exposure to real hazards. - Healthcare: Medical residents can perform virtual surgeries or emergency procedures like intubation and trauma response without risking patient safety. For example, VR airway management training allows repeated practice on rare or critical cases that can’t be simulated easily on real patients.
At Lumeto, we’ve seen how immersive simulations help medical students understand correct dosing, timing, and safety checks through hands-on repetition. This video of medication administration simulation shows how a virtual environment allows learners to make, recognize, and correct mistakes:
3. Realistic Hands-On Experience
Some situations are too rare, risky, or complex to recreate safely in real life. When there’s no way to simulate them physically, VR offers a solution. A virtual training platform can replicate everything from the sights and sounds of an emergency room to the precision of operating industrial machinery.
Realism helps learners build both technical skills and situational awareness. For example, medical students can experience the intensity of a trauma case, while technicians can practice handling machinery failures, without any real danger. A recent meta-analysis found that training in realistic virtual environments improves how easily learners transfer knowledge and skills to real-world settings.
That said, VR cannot fully replace real-world experience. It should be used in balance with traditional hands-on training and instructor-led learning.
AI is now taking this realism to the next level. At Lumeto, we’ve launched the industry’s first generative AI-powered virtual patients. Digital patients don’t just talk, but also move their body parts, react, and adjust their vitals based on student actions. Here’s an example below:
4. On-Demand, Scalable Training
Once a VR training module is developed, it can be deployed to any number of learners across different locations with minimal additional cost or logistics. There’s no need to assemble everyone in one physical classroom or schedule a specific time with an instructor. Learners can access the training on demand, whenever and wherever it fits their schedule.
Each person simply needs a VR headset (or even just a PC, if the program offers a desktop mode) to participate.
A nurse on a night shift can put on a headset during a quiet period and run through a quick refresher simulation without waiting for the next scheduled class. Similarly, companies can train new hires or upskill employees anytime without the delays of organizing in-person workshops.
At Lumeto, this flexibility is enhanced through active observer mode, which allows multiple learners or instructors to join the same virtual session in real time.
5. Enhanced Engagement and Motivation
Learners often find VR training more exciting and enjoyable (because of a game-like experience). It makes them more inclined to complete training modules and seek out additional practice. Modern learners, especially younger employees, actually expect technology-driven experiences; as one expert noted, today’s learners often enjoy tech-based learning.
Research has shown that VR learners can be far more focused and emotionally involved in the material. In one study, participants in VR training were 4 times more focused than their e-learning peers.
Companies have also observed improvements like higher employee satisfaction with training and better knowledge test scores after implementing VR learning.
6. Cost Efficiency Over Time
While VR training may require an upfront investment (for headsets, software development, etc.), it often proves more cost-effective in the long run. The reason is that VR can replace or reduce many recurring expenses associated with traditional training.
Here are some ways VR training saves costs over time:
- No recurring instructor fees: Once developed, the VR module delivers consistent training without needing live instructors for every session.
- Reduced travel and accommodation costs: Employees train locally instead of traveling to centralized training centers.
- Avoids equipment downtime: Machinery doesn’t have to be taken out of production for training purposes.
- Lower venue and setup costs: Virtual simulations replace physical classrooms and rented training spaces.
- Faster training completion: VR learners finish training in less time, reducing labor and productivity losses.
- Reusable digital content: Training assets can be used repeatedly for future employees or refresher courses.
- Scalable access: The more employees use a module, the lower the cost per trainee.
- Fewer scheduling conflicts: On-demand access cuts down on delays tied to instructor or facility availability.
- Reduced error-related expenses: Employees make and correct mistakes virtually, preventing costly real-world errors later.
7. Faster Skill Development
VR training accelerates learning because trainees can practice anytime, anywhere, and at their own pace.
Walmart, by switching to VR, cut its employee training time by 96%, reducing an 8-hour in-person session to just 15 minutes. Here’s how VR speeds up skill development:
- On-demand training: Learners train without waiting for instructors or class schedules.
- No travel or setup time: Everything happens instantly in the virtual environment.
- Instant feedback: It shortens the learning loop, helping trainees correct mistakes right away.
8. Data-Driven Performance Tracking
Traditional training can be hard to measure. Instructors might rely on tests or observation, but much of what a trainee does during a role-play or hands-on session isn’t captured.
VR training, being software-based, changes that. It automatically tracks a wealth of performance data for each learner, providing granular insight into their strengths and areas for improvement.
Every action in a VR simulation can be logged. For example, the system can record:
- How long a trainee takes to recognize a critical situation
- Whether they followed all the correct steps in a procedure
- If they skipped an important safety check
All this data is compiled into dashboards or reports. For instructors and managers, the analytics allow them to monitor progress and coaching needs. They can see, for instance, that every staff member has completed a safety drill and whether they met the proficiency criteria.
Because the training is recorded, it’s easy to demonstrate compliance and competence. Healthcare training institutes have data showing that “100% of learners completed the exercise correctly” or pinpointing exactly which step tends to trip people up.
In Lumeto, for example, the Artificial Clinical Evaluator (ACE) gives educators clear visibility into learner performance. It tracks metrics like checklist scores, session improvements, and overall proficiency trends. Here’s a dashboard view:

9. Emotional and Empathy Training
VR has a unique ability to provide experiential learning by placing learners in someone else’s shoes. The technology lets you feel the situation first-hand. In VR, you could be a doctor breaking bad news to a distraught patient, a manager witnessing a case of workplace harassment.
For example, VR simulations have been used to teach empathy in law enforcement and healthcare by exposing trainees to scenarios that require understanding another’s perspective.
One study found that police officers who underwent VR de-escalation training showed measurable increases in empathy scores afterward.
Recent research from Stanford’s Accelerator for Learning (2025) adds to this evidence. The study found that VR helped new managers build empathetic communication skills by letting them practice tough conversations in a realistic environment.
Participants took part in performance review simulations, switching roles between manager and employee. When they later reviewed the conversation from the other person’s point of view, their language shifted to include more empathy-driven words like “I” and “we,” and they expressed greater emotional understanding.
One of the most powerful ways to teach empathy in healthcare is to let learners experience emotionally charged interactions for themselves. Lumeto’s platform now makes that possible through AI-powered patient simulations that let instructors design realistic, emotionally responsive dialogues.
By editing AI conversations, educators can create lifelike patient interactions. For example, an instructor can build a scenario where a patient expresses fear about their worsening condition or curiosity about end-of-life options. Here’s an example:
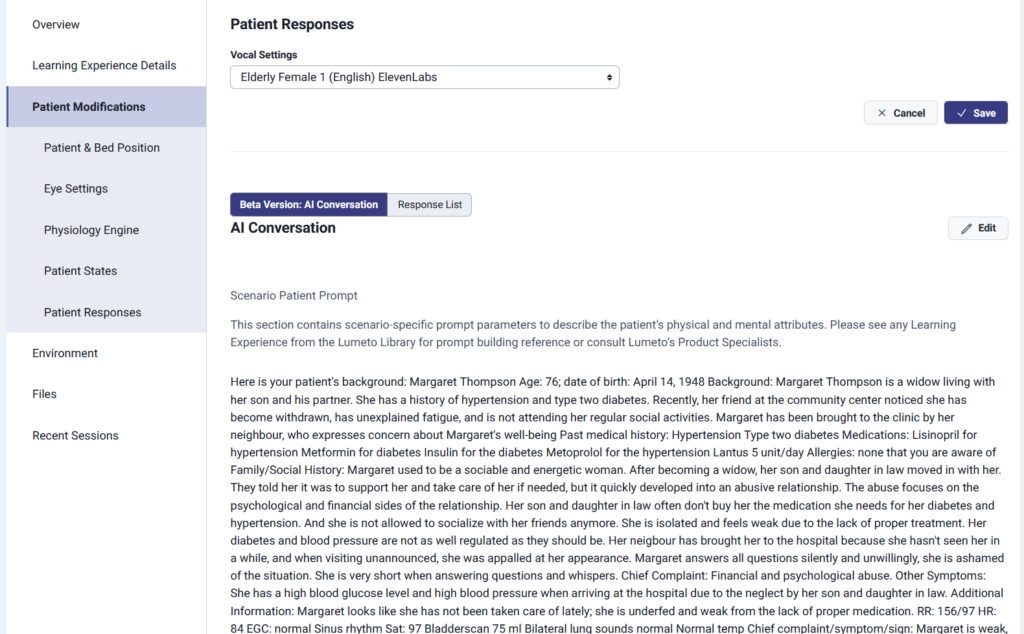
10. Sustainability
Because VR training is delivered digitally, it can significantly reduce the environmental footprint of training programs. In contrast, traditional training involves:
- Travel (commuting to training centers, or flying in instructors and trainees for conferences and workshops)
- Printed materials or manuals for each session
- Use of physical consumables or equipment that might get worn out.
Even equipment-intensive training can be virtualized. For example, at Lumeto, healthcare trainees can now receive an introductory session on ventilator setup and operation entirely in VR. Students explore the ventilator interface, adjust settings, and observe patient responses, all in a simulated environment.
Here’s an example:
11. Consistent Quality Across Learners
When training is delivered in person by different instructors or at different sites, it can be hard to ensure everyone gets the same quality of training. Variations in teacher style, facility resources, or group dynamics mean some learners might not experience the course in the exact same way as others.
This isn’t the case with VR training. But every learner who puts on the VR headset experiences a carefully designed simulation that is standardized across the board.
An organization can thus roll out a VR module to thousands of employees, knowing that each person will be held to the same performance standard. All employees or trainees will be exposed to the same situations, no matter their location.
On Lumeto’s VR training platform, this consistency is built right in. Instructors can literally copy an entire learning experience and share it across teams or campuses. That means every learner practices the same skills and gets assessed by the same metrics.

Explore the Benefits of VR for Training With Lumeto
Virtual reality is changing how healthcare professionals learn and practice clinical skills. But the real impact comes when these experiences are designed specifically for medical training.
Lumeto’s VR training scenarios are built around realistic patients, accurate procedures, and measurable outcomes. We offer the flexibility and depth modern healthcare education needs with the following features:
- Train Together or Independently: Up to five VR users can join the same simulation—either synchronously for team-based practice or asynchronously for individual skill building.
- Fully Customizable Training: Using 800+ scenario customization tools, educators can design their own training modules with specific patients, equipment, medications, and clinical environments.
- AI-Guided Tutorials: Built-in interactive tutorials guide learners step-by-step through each scenario, ensuring consistent learning even without direct supervision.
- Train the Trainers Program: Lumeto supports educators with a dedicated Train the Trainers program, helping instructors learn how to design, deliver, and evaluate VR-based learning effectively.
Lumeto can help your organization build confident, capable healthcare professionals through immersive, data-driven VR training. Request a demo today!
FAQs About the Benefits of VR Training
Is VR training suitable for all types of learners?
VR supports different learning styles (visual, kinesthetic, and auditory) by combining action, visuals, and feedback. Learners who prefer hands-on experience find it especially effective.
What are the long-term benefits of vr training solutions in healthcare?
Long term, VR improves skill retention, reduces training costs, increases confidence, and supports sustainable learning by reducing travel and material waste.
Which industries use VR for training?
VR is now used in healthcare, manufacturing, aviation, construction, energy, and education. In healthcare, for example, medical students and nurses use VR to practice complex procedures without putting patients at risk.