
VR Medical Training: Benefits, Applications, Best Practices
VR Medical Training: Benefits, Applications, and Best Practices
VR medical training lets professionals practice without real-world risks. Whether it’s diagnosing a condition, procedural training, or even getting comfortable in a hospital setting, virtual reality (VR) offers a safe space to learn and make mistakes.
This guide will explain VR medical training and how it’s being used today. We will also share some best practices for those looking to integrate it into educational programs.
What Is VR Medical Training?
VR medical training uses virtual reality technology to create immersive, interactive environments where medical professionals can practice their skills.
VR medical training companies like Lumeto are incorporating 3D interactive content and 360-degree video into their training programs. It allows learners to explore anatomy in three dimensions and experience clinical scenarios as if they were physically present.
In VR medical training, the process involves several key components. At the core is the Client VR Application, which the trainees interact with. This application includes various modules:
- VR Visualization Module: This is where the simulated environment comes to life. It includes features such as:
- Physics Simulator to replicate real-world physics,
- AI-driven Virtual Patients for realistic interactions,
- Virtual Instructors/Assistants to guide learners through the scenarios.
- Learning Analytics Module: Tracks performance data to give feedback on the learner’s progress.
- Scenario Simulation System: This system uses predefined scenarios pulled from the Scenario Database to simulate different medical situations.
- Built-in Quiz and Test Data: Provides immediate testing to assess understanding during or after the training.
On the backend, a Database Web Server manages essential data, such as 3D models of anatomy, scenarios, and user information.
Evolution of VR in Medical Training
Virtual reality (VR) started moving into the medical field in the 1990s when VR was largely associated with entertainment and gaming.
However, some forward-thinking researchers saw potential beyond it. They began to explore how VR could be used to help patients manage anxiety, phobias, and pain. These early experiments marked the first steps in what would become a revolutionary tool for healthcare professionals.
The initial success of VR in therapeutic settings opened the door to broader applications. Researchers realized that if VR could help patients confront their fears, it could also create risk-free spaces for medical professionals to practice their skills.
In 2023, Lumeto, a VR healthcare simulation company, introduced a groundbreaking AI-driven conversational system. It is powered by a Large Language Model (LLM), which enables highly realistic and adaptive virtual patient interactions.
Unlike earlier systems that relied on limited, pre-set responses, Lumeto’s innovation allows for seamless, free-flowing conversations that closely mimic real-life patient encounters. Here’s a look at it:
As we move forward, VR’s role in medical training is set to expand even further. Implementing multiplayer VR and advanced haptic feedback will enable hands-on learning across different geographies.
How Is VR Used in Medical Training?
VR for medical training offers a wide range of applications that enhance the learning experience for healthcare professionals.
Teaching Anatomy and Physiology
Anatomy is inherently a visual and three-dimensional (3D) science. Yet, it has traditionally been taught through two-dimensional images in textbooks and classroom settings.
However, the introduction of VR for medical training is changing this approach. A recent study explored the impact of incorporating VR sessions into the curriculum for nursing students. In this experiment, 254 students used VR to inspect 3D models of various human organs, allowing them to interact with these models as if they were real.
Students reported that the VR sessions significantly facilitated their understanding of complex structures. They were also highly satisfied with the overall learning experience.
Enhancing Diagnostic Accuracy
VR can improve medical diagnosis training by merging immersive visualization with real-time interaction and data analysis. The immersive approach enables understanding medical conditions and disease knowledge in previously impossible ways.
The process begins with a virtual environment where they can interact with detailed 3D models and simulations. It enables them to practice and refine their diagnostic skills in a controlled environment, reducing the need for costly lab upgrades.
Additionally, by integrating patient data directly into these simulations, VR provides an analytical layer that enhances decision-making.
Simulating Emergency Room Scenarios
Emergency room (ER) scenarios demand soft skills such as quick decision-making, clear communication, and the ability to stay calm under pressure. For medical professionals and nursing staff, managing nerves in these high-stress environments is crucial.
VR training offers a unique opportunity to prepare for these intense situations by immersing trainees in realistic ER scenarios. It allows them to practice responding to critical incidents in real time, helping to build the mental resilience needed to perform effectively when every second counts.
Here’s how medical VR simulations can help emergency department (ED) training:
- Predicting the behavior of your trainees.
- Enhancing communication skills during critical moments.
- Practicing rapid decision-making in life-or-death situations.
- Building confidence in managing high-pressure environments.
Practicing Surgical Techniques
Surgical training is perhaps the most critical aspect of medical education, with the highest stakes. A single mistake can have life-altering consequences, making it essential for surgeons to be exceptionally well-prepared.
VR training allows medical professionals to practice and perfect their techniques in a risk-free, controlled environment. Recognizing the importance of such training, more institutions will start integrating VR into their educational programs.
Developing Patient Communication Skills
Good communication builds trust and improves patient outcomes by ensuring that patients understand their diagnoses, treatment options, and care plans. VR training develops these communication skills by immersing healthcare professionals in realistic patient interactions.
Lumeto has taken this further with its InvolveXR platform, which uses generative AI to create lifelike and unpredictable virtual patients.
Here’s how virtual patients can prepare resident doctors and nurses for unpredictable scenarios:
Moreover, Lumeto’s platform allows clinical educators to design a diverse array of virtual patients that reflect different backgrounds, cultures, and personalities.
Continuing Medical Education (CME)
As medicine evolves, so must the knowledge and skills of those in the field. Continuing Medical Education (CME) ensures that doctors, nurses, and other healthcare providers maintain competency. With VR, CME can cover various scenarios, from rare surgical procedures to routine patient care.
Benefits of VR in Medical Training
Here are some benefits of implementing VR medical training programs in your institution:
Emergency Readiness
VR provides a controlled yet realistic environment where students can practice responding to emergencies. The immersive nature of VR helps trainees mentally prepare for high-pressure scenarios.
Beyond mental preparedness, VR enhances behavioral skills by allowing students to practice essential tasks, effectively training muscle memory repeatedly. This repetition ensures that the actions needed are almost instinctive when faced with real-life emergencies.
Accessibility and Flexibility
In medical VR training, students can participate in live, real-time sessions with instructors and peers. They can also complete modules at their own pace, revisiting challenging scenarios as needed.
Additionally, VR training supports both single-learner and team-based environments. Students can practice independently or as part of a team, and VR will simulate the necessary dynamics and interactions.
Moreover, training onsite or remotely adds another layer of flexibility. Whether students are in a traditional classroom, a hospital setting, or even learning from home, VR ensures they have access to high-quality, immersive training experiences.
Improved Collaboration
In a VR setting, students and instructors can engage in collaborative learning experiences, whether they are in the same room or miles apart. This technology allows for real-time interaction in shared virtual spaces. Medical teams can practice procedures, make decisions, and solve problems together as if they were physically present.
Patient Care
In the United States alone, medical errors are responsible for an estimated 250,000 deaths every year, making them the third-leading cause of death in the country. This alarming statistic underscores the importance of effective training for healthcare professionals.
Good training translates directly into good patient care, reducing the likelihood of errors and improving outcomes. By simulating real-life scenarios, VR allows trainees to learn from their mistakes without putting actual patients at risk.
Specialty Procedure Mastery
Specialty medical procedures can be challenging due to the limited availability of medical equipment. There are also ethical concerns associated with performing them on real patients.
These rare scenarios are often difficult to replicate in a traditional training environment, yet students must be thoroughly prepared when they occur in real life. VR provides a valuable opportunity for repeated practice in a safe, controlled setting.
Lumeto enhances this experience by allowing instructors to create customized scenarios with unlimited possibilities. Instructors can tailor every aspect of the simulation, from the specific medical conditions to the patient’s behavior, background, and available resources.
Reputation for Innovation
Institutes integrating VR systems into their medical training programs are positioning themselves as leaders in the healthcare industry. The commitment to innovation attracts top talent, faculty and students, eager to be part of an environment that prioritizes advanced clinical practice.
Traditional Medical Simulation vs. VR Medical Training Software
Medical training has undergone significant transformations over the years. Today, Virtual Reality (VR) is emerging as a powerful alternative, offering a level of realism and immersion that traditional methods simply cannot match. Here are a few differences:
Realism and Immersion
Traditional medical simulations typically rely on various physical and audiovisual tools to create realistic training scenarios. These elements include:
- Mannequins: Life-sized models to simulate various human functions, such as breathing, heartbeats, and basic movements.
- Mock-up Operating Rooms: Fully equipped rooms designed to mimic the environment of a real surgical setting.
- Task Trainers: Devices that replicate specific parts of the body, allowing students to practice particular procedures like suturing or intubation.
- Standardized Patients: Actors trained to portray patients with specific conditions, providing a more human element to the simulation.
In a VR environment, students are fully immersed in a 3D, interactive world where they can perform procedures, make decisions, and experience the outcomes in real time.
For instance, a VR simulation can include a distressed patient with realistic responses to the care provided (difficult to replicate with mannequins or actors).
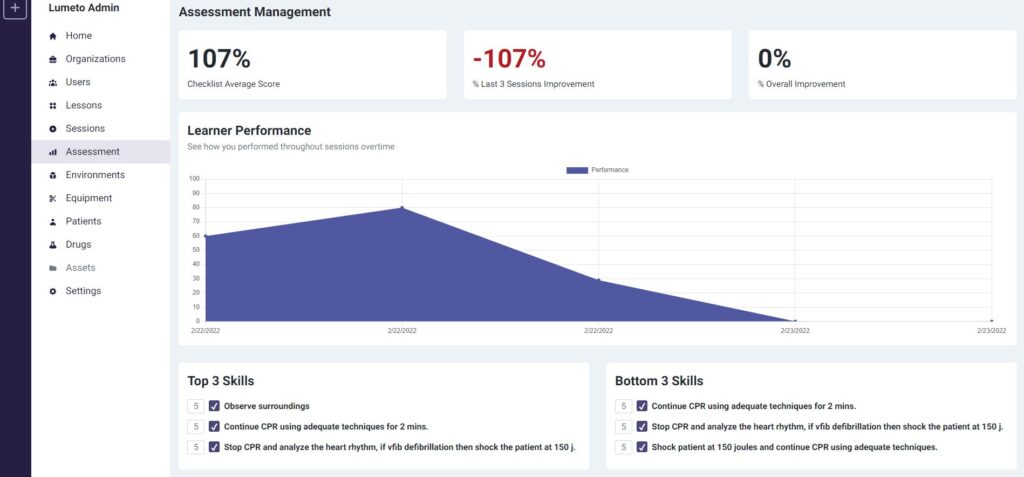
Lumeto’s Artificial Clinical Evaluator within the VR system can track a student’s performance throughout the simulation. It can also analyze their actions, decision-making, and adherence to clinical guidelines.
Repeatability and Consistency
In traditional training settings, the quality and content of simulations can vary based on factors like:
- Instructor availability,
- The condition of the physical equipment,
- The nuances of how a scenario is presented.
With VR, every student can access the same high-quality simulations, ensuring that everyone receives consistent training. Moreover, VR allows for endless repetition without degradation in the quality of the experience.
Learning Curve for Instructors
Adopting new technology often comes with a learning curve, and VR medical training is no exception. However, VR platforms are increasingly designed with user-friendly interfaces and intuitive controls, making the transition smoother for instructors.
Cost-Effectiveness
Traditional medical training, while effective, comes with a range of ongoing costs that can add up significantly over time. These expenses include:
- Mannequins and task trainers
- Mock-up operating rooms
- Standardized patients
- Facility maintenance
- Specialty procedure trainers
In contrast, VR medical training offers a cost-effective alternative. The primary expense for VR lies in the upfront investment in the technology itself—hardware, software, and content development. But, once these are in place, the costs associated with ongoing training are significantly reduced.
VR allows for creating diverse training scenarios within a single platform, eliminating the need for multiple physical setups. Moreover, updates and new scenarios can be integrated into the system without additional physical resources or space.
Feedback and Performance Assessment
In a traditional setting, feedback often relies on instructors being physically present to observe and evaluate each student, which can be time-consuming and inconsistent.
VR offers immediate, detailed, real-time feedback on performance during the simulation. VR also introduces AI-assisted evaluations that significantly reduce the burden on instructors.

Motion Sickness and User Discomfort
In traditional settings, user discomfort is generally limited to the physical demands of long hours on their feet, repetitive motions, or stress related to high-pressure scenarios.
These types of discomfort are more about physical strain and mental fatigue rather than the sensory confusion that can sometimes occur in VR.
On the other hand, VR can sometimes cause motion sickness, especially for users who are new to the technology. It occurs when there is a disconnect between what the eyes perceive and what the body feels—such as moving through a virtual environment while remaining physically stationary.
To mitigate these issues, VR systems increasingly incorporate advanced features like higher frame rates, improved graphics, and better motion tracking, which help reduce the likelihood of motion sickness.
Success Stories of VR Medical Simulation and Training
VR medical training continues to gain traction in the healthcare industry. Its impact is becoming increasingly evident through many successful case studies.
Here are some examples of how VR medical simulation is making a difference.
Empathy Training for Police Officers Using VR
Wilfrid Laurier University carried out an innovative study to assess the effectiveness of empathy training for police officers. Using Lumeto, they compared VR training against more traditional, live-action methods to see which better helped officers understand and respond to individuals in mental health crises.
The study involved 63 police officers from various Ontario services, all taking part in the Mental Health Crisis Response Training (MHCRT) program.
Results showed that officers trained in either format displayed an increase in empathy, with no significant difference between the VR and live-action groups. This outcome suggested that VR can be as effective as traditional methods for empathy-building, offering an alternative approach that is potentially more accessible and scalable.
VR-Based Airway Management Training
The CHEST Pilot Study explored the impact of VR-based training on teaching airway management—a critical skill for various healthcare professionals.
Lumeto’s immersive training comprised interactive scenarios, with groups of 2-3 learners per instructor to facilitate personalized guidance. Each learner navigated two rounds of realistic, role-swapping scenarios, which encouraged them to experience different perspectives of the situation. Sessions concluded with a detailed debrief and grading from faculty members, all within a concise 25-minute time frame.
One notable outcome of the study was the 16% relative increase in procedural knowledge after just a single 25-minute VR session. Learners who had never performed an intubation before were able to successfully complete the procedure in the VR environment.
Choosing VR Medical Training Companies
With the rapid advancement of technology, numerous companies are entering the field of VR medical training.
Here’s how to choose the right VR medical training company that aligns with your educational goals and operational requirements:
Technology Offerings
When selecting a VR medical training company, one of the first considerations is the technology they offer—both hardware and software. Effective VR training relies on the seamless integration of these two components.
Some platforms are designed with affordability in mind, making them more suitable for smaller institutions with tighter budgets. These solutions typically offer basic hardware setups that are easy to implement and require minimal investment.
The hardware should be user-friendly and easy to set up, and the software should be intuitive and efficient without requiring excessive bandwidth.
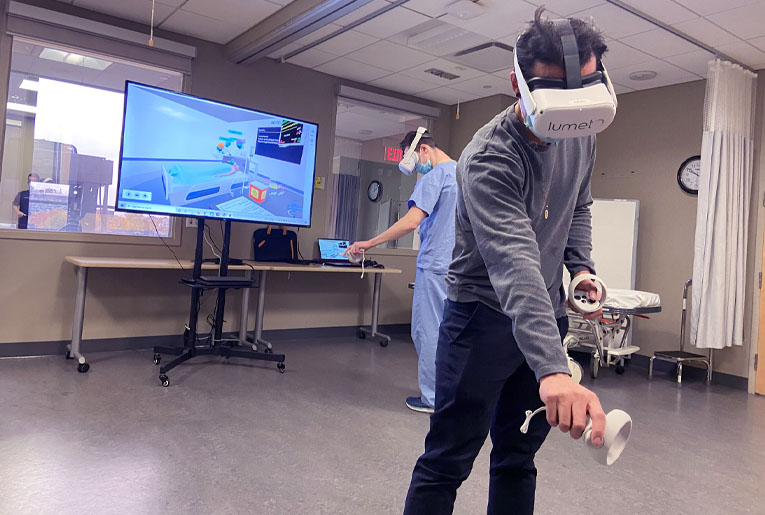
Content Customization Options
Most VR training platforms offer a set of pre-built scenarios, which can be a good starting point for many educational programs. However, these fixed modules often come with limitations. What happens when your students need procedural training not included in the list?
This limitation can be a significant drawback if your curriculum requires training for specialized or less common procedures not included in the standard offerings.
Advanced VR medical training companies, like Lumeto, allow instructors to customize and create new content. They are not confined to a predetermined set of scenarios; instead, they can develop and adjust training modules to meet their specific needs.
Support and Training Services
Even with the most advanced VR platforms, instructors can sometimes face challenges or uncertainties. It’s important to consider the level of support VR medical training companies offer.
A good VR provider will offer technical support and training services to help instructors fully use the platform’s features.
Lumeto’s team of medical industry experts, product specialists, and engineers provides comprehensive onboarding and training. We make sure that learners and instructors get the most out of the platform.
User Reviews and Case Studies
Testimonials and case studies provide insight into whether the platform delivers on its promises. If leading medical schools, hospitals, or training centers use the platform, it’s a strong sign that the technology is effective and respected in the industry.
Look for case studies that highlight measurable improvements in skills acquisition, knowledge retention, and student performance. Additionally, feedback from professional instructors who have used the platform can provide a practical perspective on its usability.
Lumeto’s users have shared their experiences as well. Dr. Timothy J. Koboldt, Associate Professor of Emergency Medicine at the University of Missouri, highlights the platform’s adaptability:
The customization is the first thing that drew me to the platform. Not only can I create states and import media ahead of time, but I can also change the vitals and states on the fly in response to what the learners are doing. The custom prompted AI conversation feature allows me to have the patient know their own history and respond naturally to questions, which increases the immersion even more.
Dr. Timothy J. Koboldt, Associate Professor of Emergency Medicine at the University of Missouri
How Lumeto Helps Medical Instructors
Lumeto provides tools that are designed to enhance the teaching and learning experience without overwhelming the user. We have the largest library of Immersible Learning Experiences. Instructors can find a wide range of scenarios that can be easily tailored to meet the specific needs of any curriculum.
Lumeto’s VR software is complemented by straightforward and user-friendly tetherless headsets for educators and learners.
These systems are particularly beneficial in environments with limited space or low-bandwidth internet. Using Lumeto’s tech, instructors can focus on what they do best—teaching—without being bogged down by technical difficulties.
As Kimberly Workum from the Rady Faculty of Health Sciences at the University of Manitoba shares:
Working with AI patients in Lumeto evokes an emotional response that mirrors interactions with human patients. The joy of making a breakthrough in patient communication or the sadness felt during a patient's distress highlights the system's realism and immersiveness. This emotional engagement makes each simulation a powerful tool for honing empathetic and professional skills as a nurse.
Kimberly Workum, Rady Faculty of Health Sciences at the University of Manitoba
Frequently Asked Questions About VR Medical Training
Can VR medical training replace traditional training?
VR medical training is not meant to replace traditional methods but to complement them by providing immersive, hands-on practice in a safe environment.
How does VR medical training ensure data privacy and security for users?
VR medical training ensures data privacy and security using AI-driven simulations that rely on synthetic data rather than real patient information. It eliminates the need for sensitive patient data, safeguarding user privacy while providing realistic and effective training experiences.
How do VR medical training programs measure and validate the progress of learners?
Learner progress in VR medical training programs is measured and validated through AI-driven assessments and real-time feedback from live trainers.
How scalable is VR training for large medical institutions?
VR training is highly scalable and can easily accommodate the needs of large medical institutions. Unlike traditional methods that may be limited by physical resources or space, VR platforms can be expanded to support a large number of users simultaneously.
How does VR medical training address cultural and language differences?
VR medical training platforms address cultural and language differences by offering customizable virtual patients. These virtual characters can be tailored to represent diverse cultural backgrounds and languages.