
How Technology in Nursing Education Improves Learning
How Technology in Nursing Education Improves Learning
Research indicates that 77.3% of nursing students expect the incorporation of technology in their education. They want VR simulations, AI, and high-tech learning tools.
But here’s the question: Are training programs keeping up? Is the nursing education system evolving fast enough to meet this demand?
In this article, we’ll break down the latest advancements in nursing education technology and how they’re shaping the next generation of healthcare professionals.
7 Key Technologies Transforming Nursing Education
In the U.S., surveys show nursing programs are adopting advanced technology faster than general education programs. Here are some digital tools for nursing education used by nursing institutions:
Virtual Reality (VR) Simulations
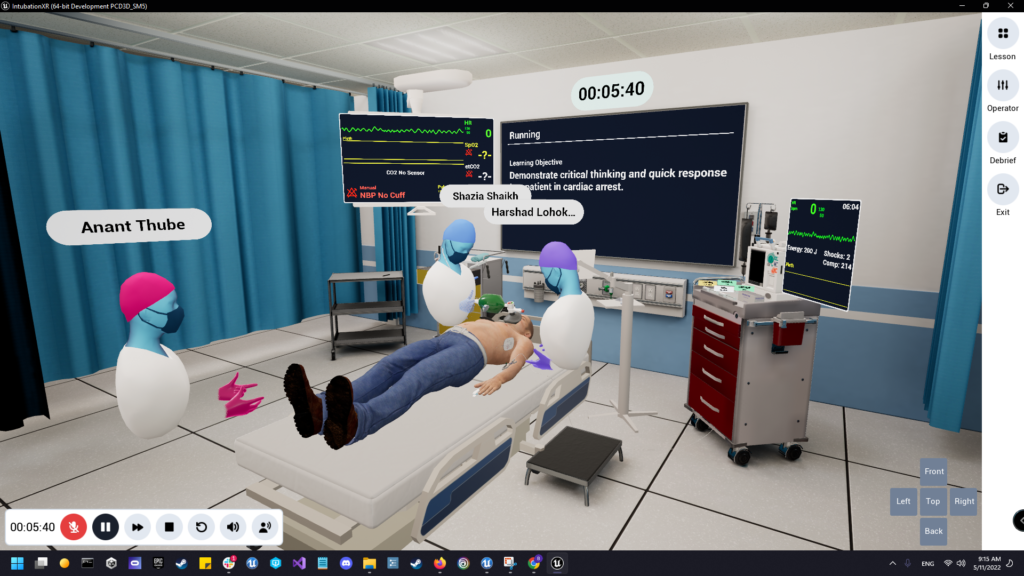
Nursing education is shifting toward immersive experiences. VR simulations provide realistic, hands-on training in a controlled environment for nursing students.
The use of videos for skills development will drop from 84% to 56% in the next five years, while virtual reality adoption will jump from 10% to 45%.
By 2023, 34% of surveyed U.S. healthcare organizations had implemented VR, with another 43% planning to do so.
Virtual reality training doesn’t replace hands-on training but complements it by allowing repeated, risk-free practice in high-stakes situations. It typically includes:
- Emergency response scenarios
- Procedural practice
- Clinical decision-making
- Interdisciplinary collaboration
- Patient interaction training
General education research shows VR training yields retention rates up to 75%—far higher than traditional lectures (5%) or reading-based learning (10%).
Lumeto’s VR Role in Advancing VR Nursing Training
Lumeto is an advanced VR training platform that enhances nursing education through immersive, AI-driven simulations. It allows students to practice clinical skills in realistic virtual environments. Nursing students can interact with AI-powered patients and collaborate with peers in multi-learner scenarios.
On Lumeto, AI-powered virtual patients respond dynamically to interventions. They reinforce clinical reasoning by mimicking real physiological changes.
A prime example of VR’s impact is a program developed by TMU alumna Halyna Yurkiv in collaboration with Lumeto, a leading healthcare training platform for nurses. This VR-based simulation trains nursing students to manage respiratory distress emergencies—one of the most high-pressure situations in patient care.
Using Lumeto’s virtual reality training, nursing students can:
- Respond to alarms signaling respiratory failure.
- Monitor vital signs in real time.
- Select the right tools and interventions to stabilize a virtual patient.
Watch how VR gives nursing students a realistic, engaging way to practice clinical decision-making:
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI is the most talked-about technology in nursing education, though it’s still in the early stages of widespread implementation. Its potential lies in automation, personalization, and real-time feedback.
Here are some key areas where AI is being implemented in nursing education:
- AI Characters: Interactive, adaptive patient simulations that respond based on student input.
- Personalized Learning Algorithms: AI-driven platforms tailor coursework based on individual strengths and weaknesses.
- Automated Skills Assessment: Real-time analysis of clinical decision-making, offering instant feedback on performance.
- Spaced Repetition & Adaptive Learning: AI optimizes when and how students review material to boost long-term retention.
- AI-Assisted Clinical Decision Training: Virtual scenarios that guide students through differential diagnosis and treatment choices.
- Predictive Learning Analytics: AI identifies struggling students early, allowing for targeted intervention.
AI has already shown strong potential to keep students engaged and reduce boredom that leads to forgetting. Spaced repetition algorithms also make sure learning is reinforced at optimal intervals.
Educators emphasize that AI should enhance—not replace—active learning. Real-world experience and human interaction are still critical in nursing education.
Lumeto has introduced the industry’s first conversational AI in VR for patient communication. This lets educators create custom AI patients that offer:
- Multi-learner scenarios: Students interact with AI-driven patients in team-based training.
- Multi-language support: AI patients communicate in different languages to improve cultural competence.
Take a look at one of the AI patients in action:
Lumeto integrates AI-driven assessment tools to simplify evaluation for nursing educators. Instead of relying solely on manual observations, instructors can track student performance with data-driven insights.
The Lumeto assessment dashboard (shown below) captures detailed checklist scores, CPR metrics, and event logs.
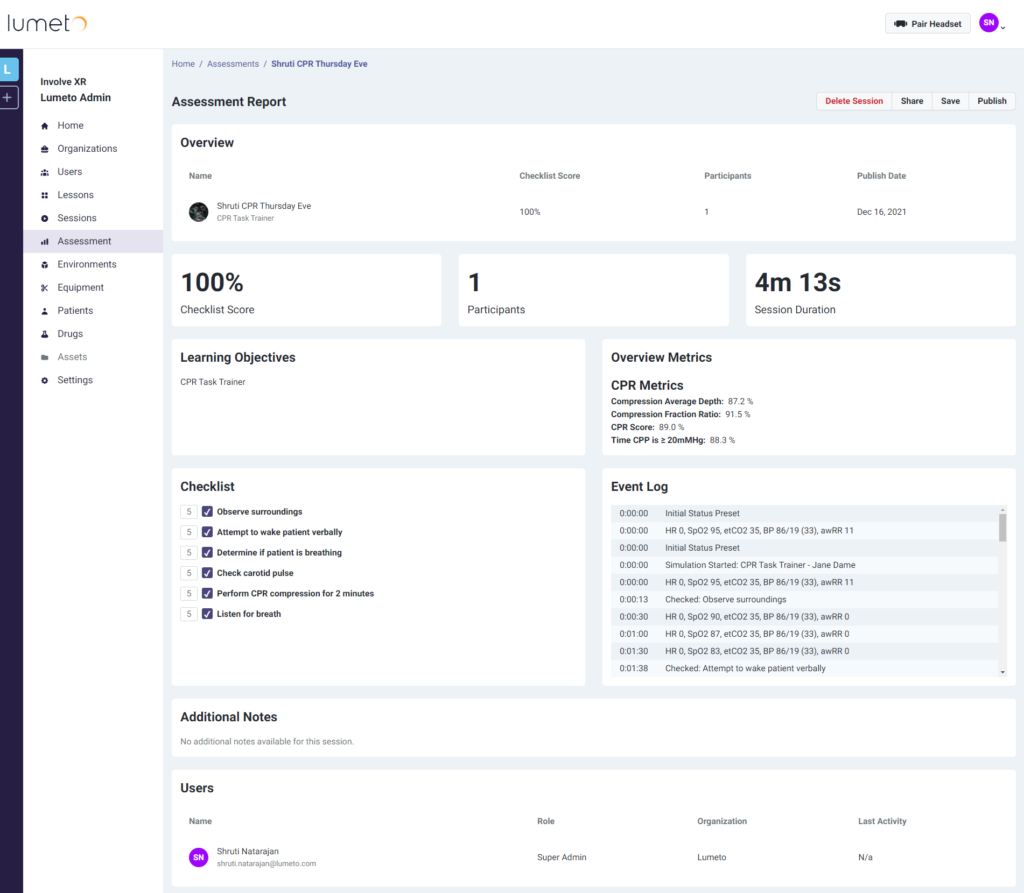
Here’s how Lumeto’s AI makes nursing education assessments more efficient:
- Automated Performance Scoring: AI evaluates student actions against predefined training objectives, generating real-time scores.
- Comprehensive Skill Tracking: The dashboard records every step taken in a simulation, from checking vitals to administering interventions.
- Objective Feedback for Improvement: AI highlights strengths and weaknesses, allowing students to reflect on their decisions and improve critical thinking.
- Time-Stamped Event Logs: Every action is logged, providing instructors with an accurate breakdown of the student’s clinical decision-making process.
E-Learning Platforms
Before 2020, e-learning in nursing education looked very different. Most programs used a hybrid model—in-person training and remote learning. Theory classes worked well with online modules. RN-to-BSN programs were already remote, but fully online pre-licensure nursing programs were almost unheard of.
Then, the pandemic hit. Spring 2020 changed everything. Nursing schools across the U.S. had to pivot overnight for accessibility. Lectures moved to Zoom. Simulation in nursing education became virtual. Assignments were handled through Canvas and Blackboard. Suddenly, nearly every nursing student was using online learning platforms in some form.
Now, research shows that self-directed learning and cyber-class flow (level of engagement in online sessions) impact student satisfaction and success. Asynchronous options allow students to balance education with work, family, and clinical rotations.
Mobile learning in nursing is another progressive area. With the proliferation of smartphones and tablets, nursing students can now access a plethora of resources, coursework, and real-time interactive modules.
Human Patient Simulators
Simulation-based training has been part of nursing education for decades. Manikins and task trainers help students develop procedural skills before working with real patients. The first computer-controlled patient simulator (Sim One) was developed in 1966 at the University of Southern California. Since then, simulators have advanced dramatically.
Examples of Modern Patient Simulators:
- High-fidelity manikins
- Birthing simulators
- Task trainers (Partial-body models for specific skills)
- Pediatric and neonatal simulators
- Trauma simulators
Human patient simulators improve clinical confidence, directly impacting patient care. A 2021 study of fifth-year medical students found a notable increase in self-confidence after high-fidelity simulation training.
Electronic Health Record (EHR) Training Systems
Electronic health record (EHR) training is now a standard part of technology in nursing education. These systems teach students to document patient care, track medical history, and follow hospital workflows before entering clinical practice.
Some trainees use academic EHR platforms in simulation labs. Others train on live hospital EHRs under supervision during clinical rotations.
A Wolters Kluwer article highlighted that electronic health records training helps students:
- Avoid documentation errors that could impact patient care.
- Develop the habit of accurate charting—“if you didn’t chart it, it wasn’t done.”
- Improve efficiency by learning to navigate EHR systems before entering the workforce.
Nursing educators see the impact. Surveys show that new grads with electronic health records experience adapting faster to hospital documentation systems. They have shorter learning curves and are more efficient in charting after orientation.
Wearable Biometric Sensors
Wearable biometric sensors are interactive training tools that enhance nursing education by simulating real-life physiological experiences. These devices help students develop clinical, technical, empathetic, and soft skills.
Wearable simulators replicate medical conditions using haptic feedback and biometric tracking. Some monitor vital signs like heart rate, stress levels, or oxygen saturation, while others create physical sensations that mimic patient symptoms.
Here are some examples of wearable biometric sensors in nursing education:
- Geriatric simulation suits: Restrict mobility and sensory perception to replicate aging-related challenges.
- Wearable birthing simulators: Worn by an actor to simulate the physical intensity of labor and childbirth.
- Wearable wound moulages: Sleeves or patches that simulate ulcers, burns, or other injuries on standardized patients.
- Wearable symptom simulators: Devices like a seizure jacket that mimics convulsions for neurology training.
- Vital sign monitors & biofeedback wearables: Track students’ stress levels during simulations for post-scenario debriefing.
- Wearable urinary anatomy devices: Allow students to practice catheter insertion on a simulated anatomy while communicating with a live “patient.”
Nursing students retain information better when we actively engage our senses. For example, a student who physically feels a baby simulator passing through a birthing suit will remember the delivery process far more vividly than if they only watched a video.
Gamified Learning
Gamified learning turns nursing education into an interactive experience. It breaks up monotony, engages students, and taps into their natural affinity for technology. Many nursing students grew up with video games or smartphone apps, so game-based learning feels familiar and intuitive.
Beyond engagement, gamification improves retention. It adds competition, rewards, and real-time feedback, making complex nursing concepts easier to grasp. Students learn faster when they enjoy the process.
Socially, gamified learning injects laughter and teamwork into the classroom. Students who compete or collaborate better retain information and feel more comfortable engaging in discussions—even outside game-based activities.
Impact of Technology on Nursing Student Learning Outcomes
Blended learning in nursing education improves training and patient care in the following ways:
Increased Retention
The World Health Organization (WHO) strongly recommends high-fidelity simulations in health professional education. Evidence shows they lead to greater acquisition, retention, and transfer of both technical and non-technical skills.
For example, a 2023 study found that students using computerized cadaver tables scored significantly higher on post-lab quizzes than those who relied on traditional methods.
Improved Confidence & Readiness
The real world is unpredictable. Patients don’t follow scripts. That’s why nursing students need the confidence to handle uncertainty.
AI patients can help by responding unpredictably, forcing students to think critically. Conversational AI allows patients to:
- Describe symptoms
- React to treatment options
- Challenge students with unexpected responses.
Let’s take a look at an AI patient answering unpredictably on Lumeto’s platform:
This kind of dynamic training is directly linked to greater self-confidence. In multiple studies, most students reported feeling more prepared after simulation lab sessions.
Faster Skill Development
The faster students develop clinical skills, the sooner they can make confident, life-saving decisions. Studies show that employees can be trained up to four times faster in virtual reality (VR) courses compared to traditional classroom settings.
Digital simulation labs in nursing force students to learn by doing. There’s a lot of time saved without the delays of scheduling clinical rotations.
One of the best examples of this is Lumeto’s VR Observer Mode. This tool allows up to 50 students to participate in a single simulation, watching and analyzing a scenario in real-time.
This kind of scalability accelerates learning. More students get exposure to critical decision-making in a shorter time. Instead of waiting for their turn, students can observe multiple patient cases, see mistakes unfold, and learn from them.
Enhanced Critical Thinking
Traditional case studies present information in a structured way, often leading students toward a single correct response. But real patient care isn’t like that.
Gamified simulations can improve critical thinking. A virtual patient scenario that branches into multiple decision paths forces students to consider consequences, weigh options, and adapt—just like in a real hospital setting.
That’s exactly what Lumeto’s VR platform delivers. The simulation library includes scenarios like:
- Ectopic Pregnancy in the ER
- Recognizing and Managing a Stroke
- Severe Community-Acquired Pneumonia
- Narcotic Overdose vs. Hypoglycemia in the ER
- PEA Arrest and more.
On Lumeto’s nursing training platform, trainees engage directly with AI-driven virtual patients. They can assess symptoms and make real-time clinical decisions, as shown in the video below:
Increased Exposure to High-Risk Scenarios
Some of the most critical nursing skills come from handling high-risk, life-threatening situations. But in traditional training, students rarely get hands-on experience with these cases before entering the workforce.
With virtual reality, nursing students can experience high-risk scenarios firsthand in a controlled, repeatable environment.
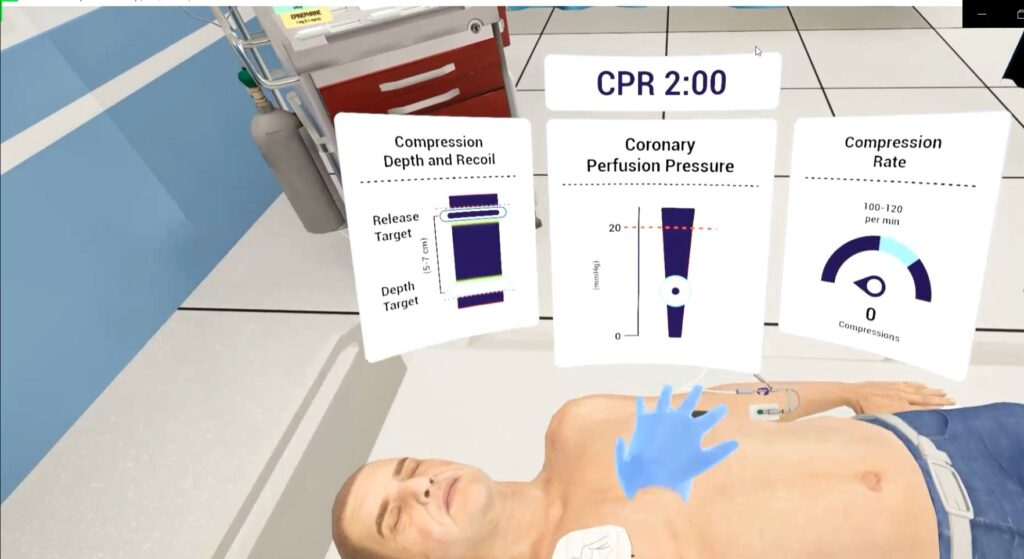
Take the CPR training simulation in the image above. This Lumeto VR scenario immerses students in an Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS) case, requiring them to deliver high-quality chest compressions while monitoring critical metrics like:
- Compression depth and recoil
- Coronary perfusion pressure
- Compression rate
But CPR is just one example. Lumeto’s VR library includes multiple high-risk scenarios that prepare students for the unpredictable nature of emergency care, including:
- Near Drowning: Managing airway obstruction and hypoxia in a water-related emergency.
- ACLS in the ER: Treating cardiac arrest patients using advanced life support protocols.
- Upper GI Bleed: Stabilizing a patient with life-threatening hemorrhaging.
- Abdominal Sepsis: Recognizing the signs of severe infection.
How Lumeto’s VR Is Helping Nursing Education
Technology and innovation are changing how nursing students train. We know traditional learning methods—lectures, textbooks, even clinical rotations—only go so far.
Lumeto is leading this transformation by recreating the real pressures of patient care. Here’s what Lumeto’s VR offers to educators and nursing students:
Virtual Patients That Respond in Real Time
Nursing students need more than scripted scenarios. They need dynamic patient interactions that adapt to their choices. Lumeto’s virtual patients exhibit real physiological responses. If a student administers the wrong medication, vitals change. If they delay an intervention, symptoms worsen.
This real-time adaptability forces students to think critically and act decisively. They experience the clinical concepts they have already learned in class and during clinical rotations.
Instructor-Controlled Simulations for Deeper Learning
Clinical exposure is limited, and nursing students can’t always practice high-risk scenarios in live settings. Lumeto’s VR allows instructors to simulate complex cases on demand, reinforcing what students learn in labs and clinicals.
Instructors can modify patient conditions in real time, challenge students with evolving symptoms, and provide instant feedback.
AI-Powered Debriefing for Smarter Assessment
Simulation is only as valuable as the reflection that follows. Lumeto’s platform tracks student decisions and provides AI-powered performance analysis. Instructors don’t have to rely on memory or subjective observation.
The system records actions, measures outcomes, and gives data-driven insights into where students excel and where they need improvement.
Here’s how nursing trainers can track students’ performance on Lumeto’s dashboard:
See how Lumeto fits into your curriculum and start training with confidence. Book a demo today!
Frequently Asked Questions About Technology in Nursing Education
Does technology help with soft skills?
Yes. Many nursing simulations now include AI-powered patient conversations and collaborative VR scenarios where students must work as a team to assess and treat virtual patients.
Can nursing students access VR training remotely, or is it only available on campus?
Many VR platforms are designed for both on-campus and remote access. With cloud-based simulations, students can train from home if they have the required hardware and internet connection.
Can VR and simulation training help reduce medical errors?
Yes. Repeated exposure to realistic patient scenarios improves clinical judgment, critical thinking, and procedural accuracy. Research shows that simulation-based learning helps students retain proper techniques and reduce real-world mistakes.