
Virtual Reality Healthcare Simulation for Medical Education
Virtual Reality Healthcare Simulation: Innovative Solutions for Medical Education
Medical training always requires a careful balance between theory and hands-on practice. Traditional training methods have served the industry well. However, as medical technology and knowledge evolve, there’s a growing need for training tools that can keep pace with innovation. Virtual reality healthcare simulation adds a new dimension to medical education. It complements traditional methods by providing a safe, immersive environment—where professionals can hone their skills in realistic scenarios.
In this guide, we’ll explore how virtual reality (VR) can work alongside established healthcare training methods to improve medical education. We’ll look at how it fills gaps and offers new possibilities for healthcare training.
What Is Virtual Reality Healthcare Simulation?
Virtual reality healthcare simulation is a technology-driven method of medical training that uses immersive virtual environments to replicate real-world medical scenarios. It allows healthcare professionals to practice and refine their skills in a controlled, risk-free setting.
The VR medical simulation market is projected to reach USD 8.5 billion by 2031, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 25.6%. It is rapidly becoming a cornerstone of modern medical education.
The concept of immersion is central to VR healthcare simulation. This technology places users in a fully interactive environment that closely mimics real-life situations.
For medical learners, this means the ability to experience and respond to scenarios as they would in a real clinical setting. Educators benefit by being able to monitor and guide these experiences, offering targeted feedback and adjustments in real-time.
How Virtual Reality Healthcare Simulation Works
Virtual reality healthcare simulation is a multi-step process that transforms traditional medical training by immersing learners in a lifelike virtual environment. Here’s how it works:
1. Creating the Virtual Environment
The process begins with the development of a detailed virtual environment. VR companies like Lumeto use advanced software to create realistic 3D models of various medical settings, such as hospital emergency rooms, operating theaters, or a patient’s home.
Every detail is carefully crafted, from the room’s layout to the appearance of medical equipment, ensuring that the environment feels as close to reality as possible.
2. Programming Medical Scenarios
Once the environment is established, specific medical scenarios are programmed into the simulation. These scenarios range from routine procedures, like inserting an IV, to more complex surgeries or emergencies.
Each scenario is designed to challenge the learner, requiring them to make critical decisions, perform tasks, and respond to dynamic changes in real-time. VR’s flexibility allows these scenarios to be easily adjusted based on the learner’s progress, providing a personalized training experience.
3. Participant Engagement
Learners engage with the simulation using VR headsets and controllers. The headset offers a 360-degree view of the virtual environment, immersing the participant in the scenario. Controllers interact with virtual objects, such as medical instruments or patient records.
Some systems even incorporate haptic feedback, which simulates the sensation of touch, adding another layer of realism to the training.
4. Educator Monitoring and Feedback
Educators can remotely monitor the learner’s actions throughout the VR-based healthcare simulation. They can observe the scenario from different angles, provide real-time feedback, and introduce unexpected challenges to test the learner’s abilities.
After the simulation, the learner and educator can review the performance, discussing what went well and identifying areas for improvement.
Virtual Reality Healthcare Simulation vs. Traditional Methods
Traditional methods of healthcare training, such as classroom instruction, textbooks, and clinical rotations, have long been the foundation of medical education.
These methods provide essential knowledge and hands-on experience, but they have limitations. For instance, clinical rotations can only offer exposure to a limited range of scenarios, and the learning experience depends heavily on the availability of real patients with specific conditions.
VR-based healthcare simulation offers a significant advantage by filling these gaps. It allows learners to experience various medical scenarios, including rare or complex cases they might not encounter during traditional training.
The repetition and standardization possible with VR make sure that all learners have the opportunity to master essential skills, regardless of their real-world clinical exposure.
Virtual Reality Healthcare Simulation vs Standard Healthcare Simulations
Traditional simulations, such as those using mannequins or role-playing, have long been integral to medical training. But they often lack the immersive and interactive qualities that make learning more impactful.
Unlike standard simulations, where the setting and scenarios can feel artificial, VR places the learner in a lifelike environment that mimics real-world conditions.
The American College of Chest Physicians conducted an IRB-approved research study on the effectiveness of Difficult Airway Management training using the InvolveXR solution. Despite 56% of learners never having tried VR before, 100% of participants understood the necessary steps as soon as they entered the virtual ICU.
Standard simulations typically require specific physical spaces, equipment, and instructors, limiting the number of learners participating simultaneously. VR, on the other hand, can be deployed remotely and scaled to accommodate many learners simultaneously.
Trainer’s Role in Virtual Reality Patient Simulation
There’s a common misconception that the rise of virtual reality in medical training diminishes the role of trainers. In reality, VR empowers trainers, enhancing their ability to guide, assess, and refine the learning process.
Facilitating Immersive Learning Experiences
Trainers set the stage by selecting appropriate scenarios that match their students’ learning objectives. Once the simulation begins, trainers act as guides, helping learners navigate the virtual environment and encouraging them to engage fully with the scenario.
They can pause the simulation to explain complex concepts, offer real-time advice, and answer questions. Moreover, trainers can introduce varying difficulty levels or unexpected challenges within the simulation to make learners adapt to new situations.
Providing Real-Time Feedback and Assessment
Real-time feedback lets medical students understand their strengths and weaknesses immediately. In VR-based simulations, the ability to assess performance as it happens is even more valuable. It makes sure that learners can correct mistakes on the spot and refine their skills in a controlled, supportive setting.
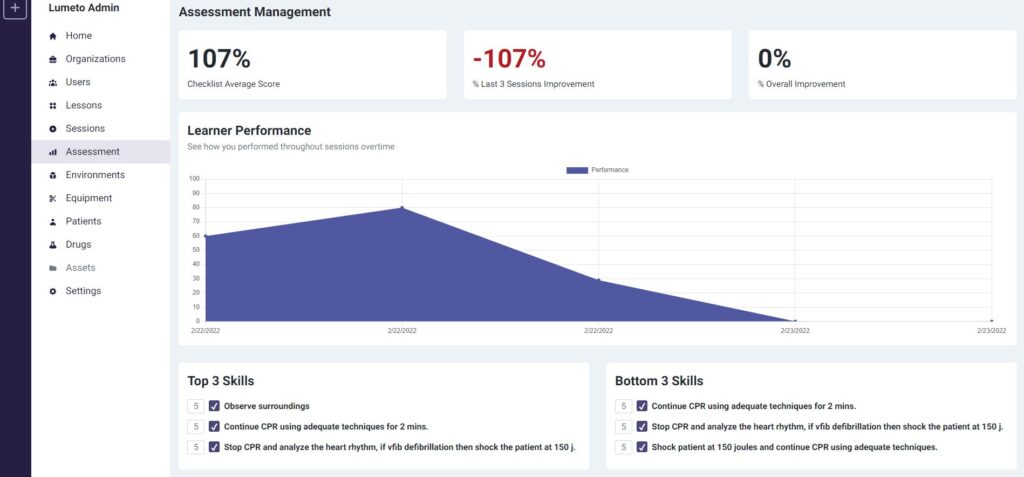
Lumeto, a leader in simulation training technology, enhances this process with its AI-assisted tools. The platform includes an Artificial Clinical Evaluator designed to work alongside instructors to streamline the assessment process.
This tool generates real-time performance metrics, helping trainers provide immediate and precise feedback. The system tracks key performance indicators, highlights top skills, and identifies improvement areas.
Adapting to Learner Needs
Instructors can fine-tune various elements of virtual reality healthcare simulation to make sure an optimal learning experience.
They can adjust the complexity of scenarios, control the pacing, and even modify patient responses to challenge learners in real time. For instance, a trainer wants to test the learner’s ability to manage stress and communicate under pressure. They can change patient vocal settings and tailor them, allowing instructors to simulate different emotional states or levels of urgency.
Instructors also can monitor and alter the virtual environment on the fly. They can introduce unexpected variables, such as sudden patient condition changes, to evaluate how learners respond to emergencies.
Bridging the Gap Between Virtual and Real-World Applications
While virtual scenarios provide a safe space for learners to practice, the ultimate objective is to make sure that these skills seamlessly translate into real clinical settings. Instructors help learners draw clear connections between a simulation and actual patient care.
It’s one thing to practice a skill; it’s another to apply it when dealing with a real person who’s scared, in pain, or just needs you to be at your best. They make sure students are not just going through the motions but understanding the ‘why’ behind each decision.
Types of Virtual Reality Healthcare Simulation
Virtual reality (VR) in healthcare simulation offers a range of applications that can enhance various aspects of medical training, such as:
Procedural Knowledge Training
Procedural knowledge is the “how-to” of medical tasks—knowing the steps to complete specific procedures accurately.
VR can help learners build and refine their procedural knowledge skills through repeated practice in a controlled, realistic setting. Unlike traditional methods, VR immerses users in lifelike scenarios, helping them build confidence through repeated practice.
Here are some examples of how VR can be used for procedural training:
- Medication Administration – Dosage Calculations
- Programming the IV Pump
- Basic Airway Management – Inpatient Alcohol Withdrawal
- Blood Product Administration
- Recognizing and Managing Rapid Afib
For instance, in collaboration with Lumeto Inc., CHEST (American College of Chest Physicians) has introduced a cutting-edge VR-based remote difficult airway management training program. This program leverages Lumeto’s InvolveXR platform and CHEST’s highly respected simulation curriculum.
Patient Interaction Simulations
VR simulations help students become more comfortable with patient communication before encountering real-life situations. Instructors can customize each virtual patient, tailoring the interaction to meet specific training needs.
Recently, Lumeto launched the first customizable AI-based system for healthcare simulations in VR. This upgrade, integrated into their InvolveXR platform, allows for free-flowing conversations with virtual patients. The AI-driven system uses a Large Language Model (LLM) to generate realistic human responses, animations, and interactions.
Learners can engage in dynamic conversations with virtual patients, where responses and scenarios evolve naturally, just as they would in a real clinical setting.
Virtual Reality Emergency Training
Stress is a constant in any emergency, and handling it effectively is crucial for healthcare professionals. While traditional training methods are valuable, they often fail to replicate the intense pressure of real emergencies.
This is where virtual reality (VR) comes in. VR allows learners to experience the urgency and stress of emergencies in a safe, controlled environment.
In VR emergency training, learners can face various high-pressure scenarios. For instance, they might manage a patient experiencing cardiac arrest, where every second counts. Or they could be tasked with stabilizing a trauma victim in a chaotic emergency room setting.
VR can also simulate mass casualty incidents, where learners must triage multiple patients and make rapid decisions about who needs immediate attention.
Critical Decision-Making Training
Medical decision-making is complex, involving several critical areas:
Number of Diagnoses or Management Options
VR simulations can present learners with various patient scenarios where they must evaluate symptoms, consider different diagnoses, and choose the appropriate management plan.
Amount or Complexity of Data Reviewed
VR simulations allow learners to practice reviewing and analyzing large amounts of data in a realistic, time-sensitive environment. The immersive nature of VR makes sure that learners are fully engaged and prioritize information efficiently.
Risk of Complication, Morbidity, or Mortality
VR provides a safe space for learners to practice assessing and managing risks without fearing real-world consequences.
Anatomy and Physiology Education
Virtual reality is changing how we teach and learn anatomy and physiology, bringing a level of interactivity that traditional methods simply can’t offer. What makes VR especially powerful is its ability to demonstrate complex processes in a way that’s both visual and interactive.
In the video below, you can see a VR setup where learners interact directly with a virtual patient.
The operator panel on the right gives options to manipulate the patient’s body—things like raising an arm, opening the mouth, or even simulating a physical response like vomiting or a limb drift.
This interactive approach is incredibly beneficial for anatomy and physiology education. It allows students to observe and engage with the body’s movements and functions in real-time. For example, by selecting different actions from the panel, learners can see how muscles and joints work together or how certain medical conditions affect physical responses.
Benefits of Virtual Reality Simulation in Healthcare
Let’s explore how virtual reality healthcare simulation benefits students, patients, and instructors.
No Risk to Real Patients
Medical errors, including misdiagnosis, are a significant risk, and the consequences can be devastating. Misdiagnoses alone result in the death or permanent disability of approximately 795,000 U.S. patients each year.
These errors often occur because medical professionals, especially those still in training, may not have had enough exposure to critical scenarios.
VR simulations allow healthcare professionals to practice and refine their skills in a controlled environment without risk to real patients. Learners can make mistakes, learn from them, and repeat scenarios until they achieve mastery—all without compromising patient safety.
Developing Psychosocial Competencies
Psychosocial competencies include empathy, communication, and the ability to manage stress. Through immersive simulations, healthcare professionals can practice and enhance their psychosocial skills in environments that closely mimic real-life situations.
Scientific studies have shown that VR can effectively stimulate emotional responses. These simulations engage the brain’s emotional and cognitive centers in ways that traditional methods cannot.
The brain processes VR experiences similarly to real-life events, meaning that the emotions and psychological responses triggered in VR are genuine.
For instance, a VR simulation might place a learner in a scenario where they must deliver difficult news to a patient or manage a high-stress situation in an emergency room.
Collaboration With Global Clinical Experts
Traditionally, gaining insights from global experts required physical travel or complex arrangements for live demonstrations. With VR, these barriers are significantly reduced, allowing for real-time collaboration and knowledge sharing across continents.
Instead of requiring a large physical space for traditional simulation labs, VR can recreate any environment—from a crowded ER to an operating theater—within the confines of a small room.
This means that a medical student in a small town hospital can learn from a leading specialist in another country and experience the same level of education and interaction as if they were in the same room.
Repeatability and Consistent Training
Different instructors, training centers, and scenarios can lead to inconsistent learning outcomes. For example, a procedure practiced under one instructor’s guidance might be taught differently by another.
Virtual reality (VR) addresses these inconsistencies by providing a standardized platform where scenarios can be repeated precisely. In VR simulations, every learner is exposed to the same conditions, challenges, and instructional content.
The repeatability of VR simulations allows learners to practice as many times as necessary until they achieve mastery. Unlike traditional methods, where resources and time may be limited, VR offers the flexibility to repeatedly revisit complex procedures or challenging scenarios.
Enhanced Skill Acquisition and Retention
In VR simulations, learners are actively engaged in the training process. They aren’t just passive recipients of information; they are fully involved in making decisions, performing procedures, and reacting to realistic scenarios.
Active participation enhances memory retention because the brain tends to remember experiences that involve direct interaction and emotional engagement better than those that don’t.
Research supports this, showing that skills learned through immersive VR training are retained longer and with greater accuracy.
How to Implement VR Healthcare Simulation in Your Institute
Here’s how to integrate VR healthcare simulation in your training institute:
Training Educators and Instructors
For VR and AI technologies to be successfully implemented, educators and instructors should understand that these tools are not here to replace them.
Instead, they are designed to make their work more efficient, effective, and impactful. VR enhances the educational process, allowing instructors to focus more on guiding and mentoring than just delivering content.
Since virtual reality healthcare simulation is relatively new, proper training for educators is essential. Lumeto’s “Train the Trainers” program is an excellent example of how to prepare instructors for this transition. The program includes multiple sessions covering all aspects of VR product functionality and deployment, as well as mock sessions designed to build practical experience.
Pilot Testing VR Training Programs
Pilot testing allows you to assess the effectiveness of the VR training modules.
To conduct a successful pilot test, select a small group of learners and educators to participate. Choose a variety of scenarios that reflect the key competencies your program aims to develop. During the pilot, feedback from both participants and instructors on the technology’s usability, the content’s relevance, and the overall learning experience will be collected.
Areas where pilot testing can be particularly useful include:
- Emergency response scenarios
- Procedural skill development
- Patient interaction simulations
- Team-based exercises
- Critical decision-making under pressure
How Lumeto’s Virtual Reality Healthcare Simulation Helps
Lumeto’s virtual reality healthcare simulation platform makes medical training as seamless and effective as possible. The average IT setup time per location is super quick, so you can get the system up and running without hassle.
Lumeto provides AI-guided tutorials that are fully interactive and embedded right into the VR environment. It means learners get to practice hands-on right there in the virtual space. No fumbling with complicated instructions or getting lost in the process.
We also have a comprehensive video library that’s your go-to resource hub. This library covers you whether you’re just starting or looking to fine-tune your expertise.
Lumeto’s refresher training sessions make sure that trainers are always at the top of their game, ready to deliver the best learning experience.
Role of VR Healthcare Simulation in Continuing Medical Education (CME)
With the global shortage of healthcare professionals, particularly in developing countries, there’s a pressing need for more effective and accessible training.
VR provides a platform where healthcare professionals can practice complex procedures. Medical professionals stay updated on the latest medical advancements without leaving their workplace.
Case studies, such as VR-based training for difficult airway management, have significantly improved knowledge retention and procedural skills. Participants can repeatedly practice high-risk scenarios safely, leading to greater confidence and competence.
Future of Virtual Reality Healthcare Technology
VR’s ability to create immersive, realistic scenarios has already significantly impacted, but what lies ahead may take medical training to an entirely new level.
AI Integration
AI is being integrated into VR platforms to enhance various aspects of training. For instance, generative AI is being used to improve patient interactions, helping students refine their communication skills by simulating realistic conversations with virtual patients.
AI-driven assessments also provide instructors with detailed, real-time feedback on learner performance.
Lumeto is leading the charge in this area with AI-driven virtual patients, bystanders, and more. These AI characters don’t just follow pre-set scripts. They react dynamically to learners’ actions and voice inputs within simulations. For example, a virtual patient might respond verbally and physically to questions asked or care provided, adapting in real-time to the learner’s decisions and tone.
AI could also analyze a learner’s emotional and cognitive responses in the future. It may offer adaptive learning paths that respond to individual strengths and weaknesses.
Expanding Access to VR Training
Traditional clinical education faces numerous challenges, particularly in developing countries, where resources, infrastructure, and access to expert instructors are often limited.
VR solves these challenges by providing a portable, scalable, cost-effective training platform. As VR equipment becomes more affordable and internet connectivity improves globally, the barriers to accessing cutting-edge medical training will continue to decrease.
Conclusion
The promise of VR lies in its ability to replicate real-world scenarios in a controlled, safe environment. Learners can practice, make mistakes, and refine their skills without risking real patients.
If you’re considering integrating VR technology into your medical training programs, Lumeto’s virtual reality healthcare simulation platform is the best option. It’s designed with the future in mind, combining ease of use with powerful tools to prepare your team for real-world challenges. Start your trial today!
Frequently Asked Questions About Virtual Reality Healthcare Simulation
What are the hardware requirements for setting up a VR healthcare simulation?
To run VR healthcare simulations, you’ll need VR headsets, controllers, and a computer. The specific requirements can vary depending on the VR platform and software you’re using, but high-resolution displays and low-latency processing are key for an effective experience.
What is the role of VR in interdisciplinary team training?
VR allows different healthcare professionals to train together in a shared virtual environment. It helps teams practice communication, coordination, and decision-making in realistic scenarios.
What are the potential psychological effects of VR healthcare simulations on learners?
VR may cause stress or anxiety in some learners, especially in high-pressure scenarios. However, it can also build resilience and confidence by exposing learners to challenging situations in a controlled environment.
Can VR simulations be recorded for review?
Yes, most VR platforms allow you to record simulations. This feature is useful for reviewing performance, giving feedback, and tracking progress.
How secure is data within VR healthcare simulations?
Most platforms use encryption and secure servers to protect sensitive information. Since the patients in these simulations are virtual and unreal, the risks associated with data breaches are lower.