
Sepsis Simulation: Benefits, Examples, and Best Practices
Sepsis is a life-threatening response to infection that affects about 1.7 million adults in the U.S. alone. At least 350,000 die during hospitalization or shortly after.
Given the urgency and high stakes, healthcare educators are increasingly turning to sepsis simulation training. Experts recommend simulation for high-acuity emergencies like sepsis because it builds practical know-how, confidence, and knowledge retention.
This article explores what sepsis simulation means, its benefits, scenario examples, and training tips. We will also look at how modern solutions (like Lumeto’s VR platform) are enhancing realism.
What Is Sepsis Simulation?
Sepsis simulation is where healthcare professionals engage in lifelike scenarios of a septic patient’s care. Learners practice the recognition, rapid intervention, and teamwork needed for sepsis care through:
In a typical sepsis simulation, participants might be presented with a patient (realistic dummy or virtual patient) showing early signs of infection and organ dysfunction. They must assess vital signs and interpret symptoms while communicating with team members.
It enables nurses and interdisciplinary teams to “practice like we play.” When a real septic patient appears, they can recognize the condition early and intervene quickly.
Lumeto is one of the leading VR-based training platforms, specifically designed for healthcare. Our sepsis simulation scenarios come with defined objectives such as:
- Recognizing signs and symptoms of sepsis.
- Prioritizing interventions based on patient condition.
- Administering a fluid bolus appropriately.
- Initiating antibiotic therapy while weighing potential adverse effects.
- Managing pain effectively alongside critical care measures.
Benefits of Sepsis Simulation Training
Sepsis simulation training offers numerous benefits for nurses, physicians, and healthcare teams. Key benefits include:
Earlier Recognition and Faster Treatment
Simulation drills train staff to spot subtle early signs of sepsis (e.g. confusion, fever, tachycardia) and act swiftly. For example, in one program, emergency nurses improved their sepsis identification time from ~38 minutes to ~29 minutes after simulation training.
Faster recognition leads to treatments (IV fluids, antibiotics) starting sooner, which is critical since each hour of delay in antibiotics increases mortality by an estimated 9%.
Simulation practice builds “muscle memory” for checking sepsis screening tools and vital signs. So that, in reality, nurses can trigger rapid response or “Code Sepsis” protocols without hesitation.
Lumeto enhances this training with dynamic patient state transitions. Instructors can design scenarios where a virtual patient improves with full treatment or deteriorates without timely action. Here’s an example:
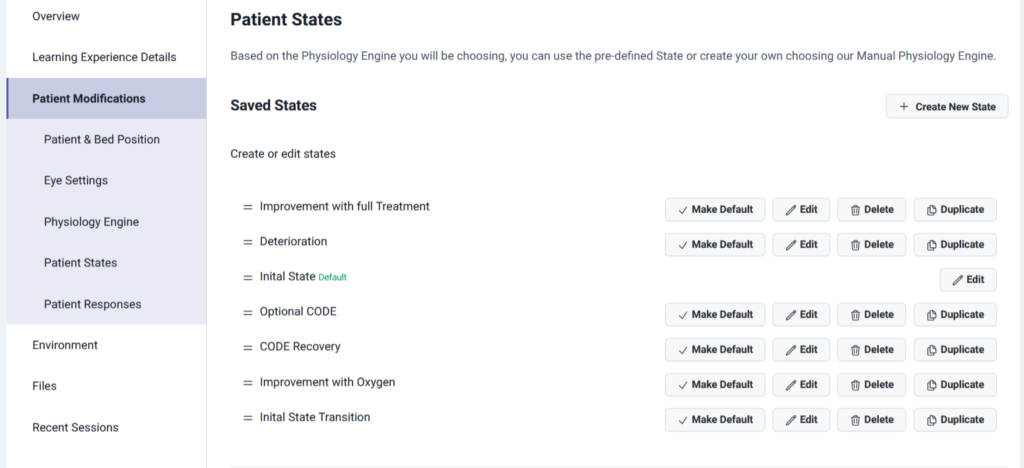
Improved Adherence to Protocols
Scenarios reinforce the evidence-based steps nurses must take within the first hour of sepsis. Research shows simulation training boosts compliance with sepsis treatment bundles.
In one study, the percentage of actions completed from the Hour-1 Bundle rose from 58% before training to 85.7% after nurses underwent combined simulation exercises.
Lumeto supports this by embedding an assessment checklist into every scenario. Learners are guided through essential steps like confirming patient identity, reviewing the EMR, administering IV fluids, and giving antibiotics. Each action is tracked, scored, and examined to measure adherence and identify areas for improvement.
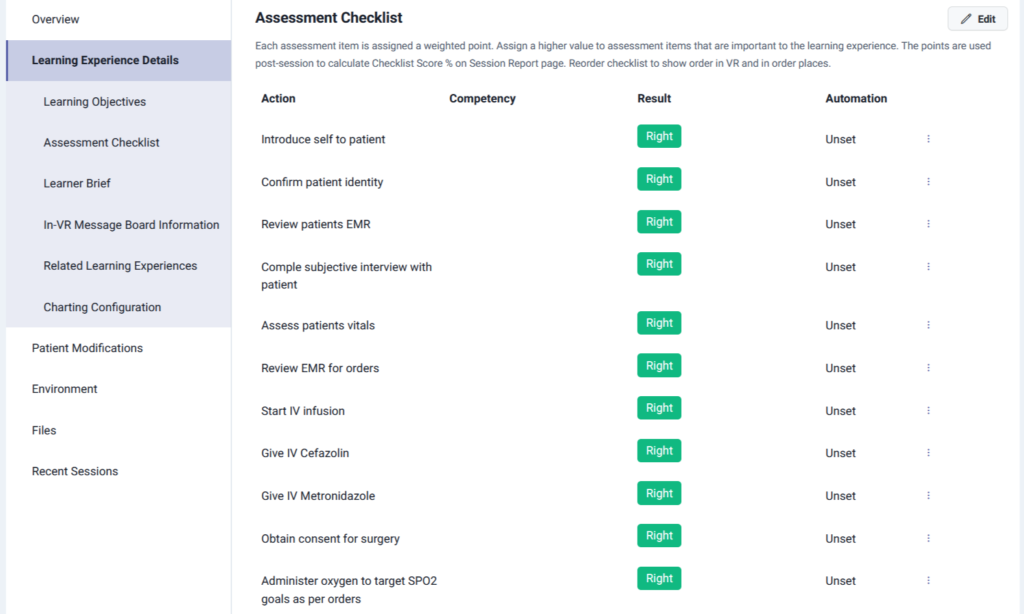
Enhanced Clinical Skills
Simulation provides hands-on practice in a no-risk setting, which builds technical skills and clinical judgment. Nurses can practice assessing a deteriorating patient and making critical decisions in the simulation.
Nursing students also report that seeing a septic shock scenario unfold in simulation helps them understand how quickly a patient can decline and how to respond: “Participating in the simulation helped me to see how the septic shock progressed… It felt real,” noted one student.
Improved Patient Outcomes
The ultimate goal is better patient care. Encouragingly, there is evidence that simulation training for sepsis translates into lives saved. Simulation-based sepsis training significantly impacts patient outcomes, including lower mortality.
By providing timely sepsis care, hospitals can expect more septic patients to survive without progressing to septic shock or cardiac arrest.
VR platforms make this training even more effective. Because all treatment occurs in a virtual setting, learners can practice high-stakes interventions. Every action feels realistic yet safe for repeated practice.
Here’s a video of a medical provider administering medication to a virtual patient:
Types of Sepsis Simulation Scenarios for Nurses
Sepsis simulations can be designed in various formats and fidelity levels, each serving different learning objectives. Here are common types of sepsis simulation scenarios:
Case-Based Tabletop Simulations
These are low-tech scenarios in which participants discuss a sepsis case progression, guided by an instructor or a written script.
For example, a facilitator might present a vignette (“Mr. X on the med-surg floor is day 2 post-op with a fever and low blood pressure… what do you do?”) and lead the group through decision-making steps.
High-Fidelity Manikin Scenarios
Many sepsis training sessions utilize a full-body patient simulator manikin in a simulation center or mobile simulation lab. High-fidelity manikins can mimic human responses (pulses, heart/lung sounds, speaking, vitals changing in real-time). In a sepsis scenario, the manikin can be programmed to start with subtle symptoms and deteriorate if proper interventions aren’t given.
In-Situ “Sepsis Drill”
In-situ simulations occur in the actual clinical environment (hospital ward or ICU) with the real staff, using either a manikin or a surprise scenario.
Many hospitals conduct “Sepsis huddles” or mock Code Sepsis drills on the floor. For example, a unit might announce a pretend scenario where a current (dummy) patient’s vitals meet sepsis criteria; the bedside nurse must then activate the Code Sepsis team. This brings together the rapid response team or designated responders (similar to a code blue team) to that unit.
Virtual Reality (VR) Scenarios
An emerging type of sepsis simulation uses VR technology to immerse learners in a 3D virtual clinical scenario. Using a VR headset and controllers, the nurse enters a simulated hospital environment. For instance, a virtual ICU room where a septic patient is in bed.
The VR scenario enables the nurse to physically examine the patient avatar by moving around the room.
One example scenario (developed by Lumeto with an Ontario nursing program) places the learner in an ER receiving a 73-year-old female in septic shock from a urinary tract infection. The virtual patient has an altered mental status, low blood pressure, and is in respiratory failure from sepsis.
Learners must manage airway and breathing, correct hypoglycemia, start IV fluids and medications – all within the virtual environment. The scenario ends when the team recognizes the need for central IV access, starts vasopressors, administers antibiotics, and prepares to transfer the patient to the ICU.
Lumeto’s patient profiles add realism by giving every virtual patient a complete history, including past medical conditions, surgeries, medications, and allergies.
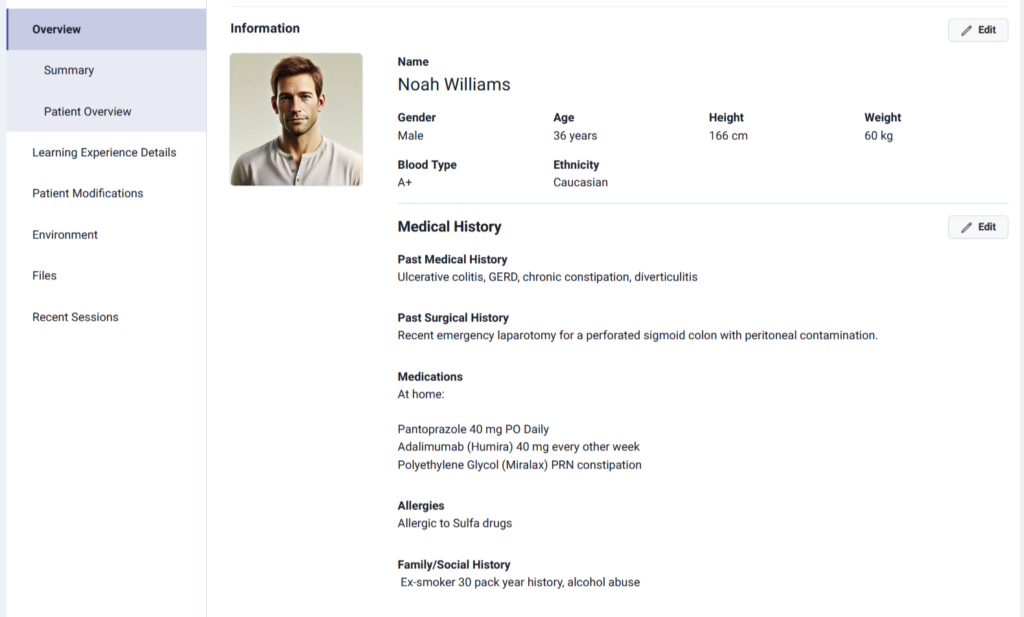
Tips for Effective Sepsis Simulation Training
Here are some tips and best practices to maximize the effectiveness of sepsis training sessions:
Create Realistic, Relevant Scenarios
Ensure the scenario content mirrors real-life sepsis cases that the nurses are likely to encounter.
Use patient profiles that make sense (age, comorbidities, typical sources of infection) and progress the case plausibly. Unrealistic or overly contrived scenarios can frustrate learners or confuse them about priorities.
For example, it’s realistic to simulate an elderly pneumonia patient who slowly worsens, but throwing in an outlandish curveball (like an exotic disease) in a basic sepsis training might distract from core learning. Incorporate actual hospital protocols and equipment to increase realism.
Lumeto introduces students to AI-powered virtual patients. Instructors can dynamically adjust patient responses during the scenario. For instance, altering speech, vital signs, or symptoms based on the learner’s actions. Here’s an example:
Facilitate a Thorough Debriefing
The real learning in simulation happens during the debrief. Setting aside time after each scenario gives participants a chance to reflect openly in a non-judgmental environment. Educators can guide the discussion with prompts such as:
- “What went well in managing this sepsis case?”
- “What challenges did you face?”
- “What would you do differently next time?”
Debrief is also a chance to tie back to real cases: e.g., “If this were a real patient, by doing X, you likely prevented them from progressing to septic shock, which improves their survival”.
Lumeto strengthens this process with AI-powered ACE (Artificial Clinical Evaluator). As shown in the dashboard below, ACE automatically tracks learner actions and flags whether they were done safely. It helps instructors pinpoint where learners excelled and where they hesitated.
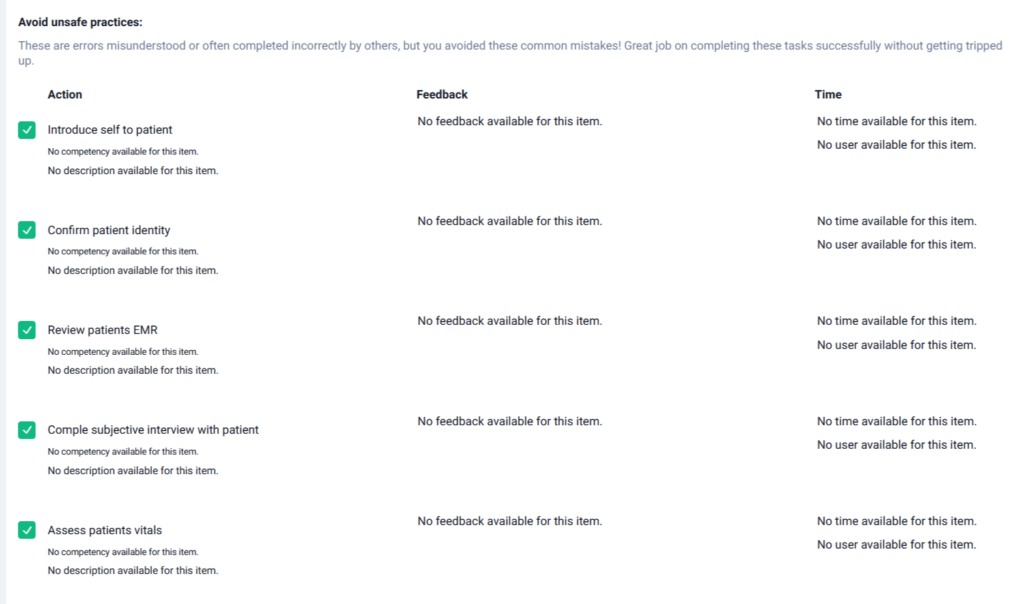
Incorporate Repetition and Variation
Don’t make sepsis simulation a one-and-done event. Skills improve with practice, and scenarios can be varied to cover more ground. Consider doing an immediate repeat of the scenario or a similar one after feedback.
Studies have found that when nursing students repeated a septic shock sim shortly after the first run, their performance and confidence improved markedly.
Ensure Safety and Psychological Comfort
While simulation itself poses no risk to patients, participant safety (physical and psychological) must be considered. Physically, ensure the environment is safe (no uncapped needles being used on manikins, equipment in working order to avoid mishaps, etc.). More importantly, psychological safety is key: learners should feel comfortable to engage fully without fear of humiliation.
It’s crucial to remind them that this is practice. Making errors in simulation is expected and even welcome (so they’re not made later on with real patients).
VR is powerful for creating this safe learning environment. Unlike manikin-based training, VR scenarios enable learners to fully immerse themselves in high-stakes cases without concern for harming a patient or being judged by peers.
The video below shows providers using Lumeto’s VR headsets to manage virtual patients while a facilitator observes in the background.
Common Mistakes in Sepsis Training for Nurses
Here are some frequent mistakes or challenges observed in sepsis training programs for nurses, and how to avoid them:
Insufficient Preparation of Facilitators
Occasionally, the issue lies not with the participants but with the simulation facilitators. If those running the sim (instructors or lab staff) aren’t well-prepared, the scenario can lose credibility. Technical glitches like monitor malfunctions or a confederate (actor) who improvises inconsistently can confuse learners.
Facilitators should thoroughly pilot test scenarios and be familiar with the sepsis content and the simulation equipment.
Lumeto addresses this challenge through our Train the Trainers Program. The program includes multiple structured sessions that walk facilitators through product functionality, deployment, and sepsis-specific scenarios. Mock sessions provide trainers with hands-on practice in running simulations. Interactive resources and virtual models enable them to guide learners confidently.
Overlooking Emotional Support
A common mistake in simulation is overlooking the emotional dimension of patient care. Traditional simulations often focus on clinical tasks (vital signs, lab values, medications) while missing the human aspect that nurses face daily. Learners may not get to practice handling fear, anxiety, or frustration expressed by real patients and families.
On VR platforms like Lumeto, this gap is addressed. Virtual patients don’t just present clinical symptoms; they also display emotional cues, such as anger, worry, or confusion, often accompanied by a realistic tone of voice and even hand gestures. Here’s a demo below:
Inadequate Feedback or Debrief
A simulation without a proper debrief is a huge missed opportunity. Some programs rush through or skip debriefs due to time constraints, or facilitators only provide vague feedback.
Without specific feedback, participants might not realize mistakes they made or might feel their efforts weren’t appreciated. In worst cases, a lack of discussion can leave learners with false confidence or lingering uncertainty.
On Lumeto, automated feedback is provided on both unsafe practices and missed safe actions. For example, if a learner discharges a septic patient too early, the system highlights the error, explains why it’s unsafe, and even links to evidence-based resources.
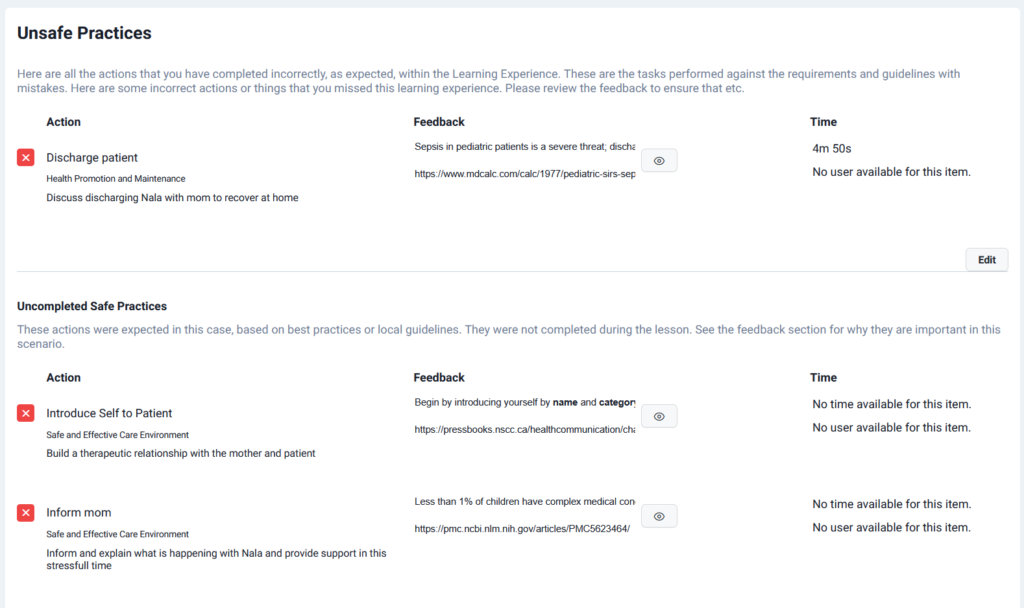
Lumeto Provides Realistic Sepsis Simulation Scenarios
Lumeto is a VR-based training platform designed to bring clinical realism into nursing and healthcare education. It enables learners to practice recognizing and treating sepsis in safe and immersive environments. Here are some of its notable features:
Remote and Scalable Training
Lumeto allows organizations to train learners anywhere, making it especially valuable for large nursing programs in North America where clinical placements are limited. Sessions can include up to 50 non-VR observers, enabling remote participation and group learning.
Highly Immersive Modular Environments
With more than 800 customizable tools and 200+ interactive medical equipment items, Lumeto creates lifelike hospital, home, and outdoor scenarios. Learners can practice in varied, high-fidelity environments that reflect real clinical complexity.
Here’s an example of an instructor giving an introduction to a ventilator in a VR scenario on Lumeto:
Seamless Setup and Low-Cost Equipment
Only a consumer-grade VR headset (Meta Quest 2 or 3), a laptop, and basic Wi-Fi are required. Average setup time is just two hours per location, and Lumeto provides support with configuration, troubleshooting, and multi-site deployment.
Flexible Training Modes
Lumeto supports instructor-led simulations, self-directed skills training, and active observer participation. With features like Record & Replay, instructors can adapt scenarios on the fly and use detailed logs for powerful debriefing.
Lumeto makes sepsis training more realistic by combining immersive VR with AI-powered patients. It helps learners recognize and respond to sepsis safely. Book a demo to see Lumeto’s VR training platform.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does sepsis simulation differ from code blue simulation?
Code blue simulation trains for cardiac arrest emergencies (CPR, defibrillation, ACLS), while sepsis simulation focuses on early recognition and treatment to prevent patients from reaching that stage.
What equipment or resources are needed for a sepsis simulation?
It depends on fidelity. A high-fidelity setup may include a manikin or virtual patient with monitors, IV lines, medication props, and a sepsis “kit” with lab slips and antibiotic labels. Many centers also use checklists, speaking manikins, or in-situ hospital setups.
Who should be included in sepsis simulation exercises?
Sepsis care is team-based, so simulations work best when interprofessional (nurses, physicians, NPs/PAs, pharmacists, and respiratory therapists).
How often should we conduct sepsis simulation training?
There is no one-size-fits-all answer, but many experts recommend incorporating simulation into education as a regular, ongoing part of the curriculum rather than a one-time event. Some hospitals integrate mini sepsis drills into their schedule every few months or at least annually for all acute-care nurses.