
VR Pediatrics: How It Works and How to Train Your Team
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the number of children in the United States is expected to reach around 76 million by 2030. With more children comes a growing demand for skilled pediatric healthcare professionals. We need better pediatric training methods for those healthcare professionals.
VR pediatrics training changes the way healthcare providers learn. It allows them to practice high-stakes scenarios without putting real kids at risk.
In this article, we’re breaking down how the VR pediatrics training works and how to roll it out inside your existing training program.
What Is VR Pediatrics?
VR pediatrics is a simulation-based virtual reality training tool for pediatric residents, nurses, and healthcare staff. It puts trainees inside realistic pediatric scenarios with AI-powered characters without the risk of working on a live patient. They can get real-time responses, emotional reactions, vital signs that shift, and situations that escalate.
Trainees can also interact and engage with the AI patients’ parents or guardians to address their concerns and explain medical procedures.
A VR pediatric simulation for healthcare trainees typically includes:
- Realistic pediatric patient scenarios (for infants, toddlers, and adolescents)
- Caregiver interaction, including parent/guardian dialogue and emotional dynamics.
- Customizable scenarios, from routine checkups to full-blown pediatric emergencies.
- Instant feedback on clinical decisions and communication techniques.
- Multi-user capability.
- Built-in metrics to track skill development.
Lumeto is the world’s leading pediatric VR training platform. It includes customizable AI characters that respond verbally and non-verbally in real time. Check out the sample scenario video below:
Applications of Virtual Reality in Pediatric Care
In most programs, VR is used as adjunctive education. It doesn’t replace clinical rotations or classroom learning. It adds to them. Here’s how virtual reality is enhancing pediatric care training:
VR in Pediatric Emergency Care
Pediatric emergencies are unpredictable. With VR, clinicians can walk through these high-pressure situations over and over until their response becomes second nature.
For example, think about dehydration in toddlers. It’s easy to miss in the early stages and dangerous when severe. In a virtual simulation, trainees assess symptoms, choose interventions like IV fluids or oral rehydration, and watch how the patient responds. They also learn to answer questions about medical procedures and face emotional pressure.
Lumeto takes this further by introducing VR patients powered by conversational AI. They can make any pediatric emergency care scenario more realistic and trainable.

Critical Care Training
Virtual reality pediatrics allows trainees to spot early red flags in AI patients’ conditions. They practice reading vital signs, assessing mental status changes, and making calls like escalating respiratory support or prepping for intubation.
In a typical ICU scenario, a virtual patient might show early signs of sepsis or deteriorating respiratory function. The trainee must interpret the data, learn intervention, and communicate with the virtual care team.
With Lumeto, instructors can go beyond static training scenarios. They can adjust a patient’s vitals and condition in real time, responding to learners’ actions. This makes the training as unpredictable and dynamic as real-world clinical situations.
As Dr. Tim Koboldt from the University of Missouri puts it.
"Not only can I create states and import media ahead of time, I can also change the vitals and states on the fly in response to what the learners are doing... I think the importance of this cannot be overstated..."
Dr. Tim Koboldt from the University of Missouri
Communication with Children and Families
A study found that over 85% of parents ranked inter-professional communication as critical regarding diagnoses, treatment plans, medications, and regular updates. But many of those same parents said that kind of communication rarely happens as it should.
In a virtual environment, healthcare teams engage with digital family members who ask hard questions or struggle to understand medical language. Providers must think on their feet, explain things clearly, and show empathy.
VR simulations often include training on moments like these:
- Delivering bad news to a parent or caregiver
- Explaining complex conditions in simple, clear language
- Walking families through next steps or discharge plans
- Clarifying medication instructions and side effects
- Responding to frustration or emotional distress
Lumeto has introduced the industry’s first VR patients powered by conversational AI. Trainers also have access to customizable non-patient characters—such as parents, caregivers, or nurses—who can:
- Ask questions based on the learner’s responses.
- Show emotional reactions like confusion, concern, or frustration.
- Deny the treatment offered.
- Require follow-up explanations in plain language.
- Create unpredictable, real-world communication challenges.
Team-Based and Interprofessional Training
Knowing the clinical role is only half the job. Healthcare providers must also know how to collaborate, communicate, and trust their team when the pressure is on.
That’s where virtual reality offers a major advantage. It creates space for true interprofessional education (IPE), where multiple disciplines train together on the same pediatric scenarios.
Take Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS) as an example. During a pediatric code, nurses, physicians, and respiratory therapists all have critical roles (managing the airway, administering medications, or leading the code.
Here’s a video of NYU students going through an ACLS session on Lumeto:
Benefits of Pediatric Virtual Reality for Healthcare Teams
Let’s break down the specific benefits of VR technology for pediatric procedures:
Enhanced Learning and Retention
The long-term impact of VR shows up in real clinical results. At Cincinnati Children’s, newly hired PICU nurses who completed VR training showed better engagement and stronger recognition of early respiratory failure—even three to six months after their sessions.
As Dr. Samreen Vora, medical director of the Children’s Minnesota Simulation Center, says, “When you give a lecture, people learn things, but it’s usually not as much and not as sustained. Simulation helps people build muscle memory and better behaviors through practice.”
Realism and the level of accuracy in a VR environment play a big role in how well learners retain information and apply it later. Lumeto focuses heavily on this, offering detailed, lifelike simulations that mirror real pediatric care settings. Here’s an example:
Exposure to Rare or High-Risk Cases
Some of the most critical scenarios are also the least common in pediatrics. For example, less than 1% of newborn deliveries require intensive resuscitation. In a small hospital, that kind of neonatal code might only happen once every few years. But when it does, the team needs to be ready.
Virtual reality closes that gap. It brings those high-risk, low-frequency intervention cases into medical training. Michael Ferguson, M.D., a pediatric intensivist at Barbara Bush Children’s Hospital, puts it clearly: “If you don’t practice something every three months, you lose skills very quickly.”
On platforms like Lumeto, instructors can simulate these rare events and adjust variables in real time. The trainer interface shows that facilitators can control patient vitals, actions, and outcomes during the session.

Risk-Free Practice
Medical errors are still one of the leading causes of pediatric deaths in hospitals. Nearly 4,500 children die each year in the U.S. due to preventable mistakes.
Virtual reality allows healthcare teams to practice medical procedures in a space where failure doesn’t cost lives. Trainees can attempt things they might hesitate to do on a real child. No real harm is done if they make the wrong call in a virtual reality scenario. But the lesson sticks.
Scalability and Convenience
Traditional simulation labs are expensive, limited by location, and often booked solid. VR democratizes pediatric training by removing those barriers.
Healthcare professionals in rural or underserved areas can now access the same high-fidelity scenarios as large academic centers. And that matters, especially when you consider that around 65% of U.S. school districts don’t have a pediatrician.
How to Train Your Team With Pediatric VR Simulations
Pediatric VR simulations don’t replace traditional education—they go side by side with it. Here’s how to do it right.
Align VR Modules with Curriculum Goals
Start by running a needs assessment. What are the specific gaps in your pediatric training program? If residents consistently feel unprepared during pediatric codes or if bedside nurses struggle with pediatric airway management, those are areas where VR can make a measurable impact.
Look at recent performance evaluations, clinical incidents, or student feedback. Use that data to match VR modules to the training pain points you’ve already identified. The more targeted the simulation, the more valuable the outcome.
Lumeto has developed and published over 100 immersive learning experiences. With 800+ easy customization tools, trainers get to create unlimited simulations. The scenarios can be aligned with specific curriculum goals, learner levels, and clinical priorities.
Educators can also easily select from a wide range of patient profiles to match specific training objectives. The screenshot below shows Lumeto’s patient setup screen:
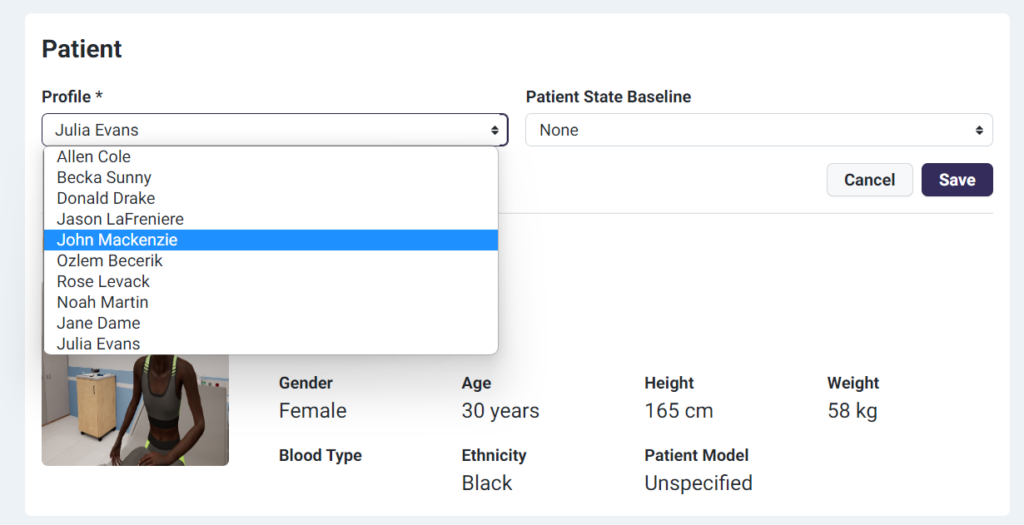
Prepare Learners
Don’t assume that younger trainees are automatically VR-ready. Even millennial and Gen Z healthcare professionals need quick onboarding to become comfortable using VR in a training environment.
Start with a short orientation. At the very least, guide learners through headset controls, adjusting fit (especially for those with glasses) and calibrating the screen properly.
At the University of Padova, students got a 15-minute intro before starting their pediatric scenarios. They didn’t jump straight into emergencies. Instead, they used the Oculus headset in a low-stress tutorial where they picked up rubber ducks and practiced basic navigation.
You can even add a warm-up fun game like Keep Talking and Nobody Explodes. It forces learners to communicate clearly with someone seeing something they can’t.
Iterative Feedback
When introducing pediatric virtual reality simulations, it’s smart to start small. Treat the rollout as a pilot and conduct quality assessment. Begin with one or two targeted scenarios, gather feedback, refine the experience, and scale.
Open-ended responses from learners can highlight what’s working and what’s not. Maybe the scenario felt too short. Maybe they wanted more time to ask the virtual parent questions. Use that input to fine-tune everything from pacing to difficulty level.
On a bigger scale, you’ll want to track whether the training is actually improving performance. Are learners getting faster at recognizing pediatric emergencies? Are scores moving in the right direction over time?
Platforms like Lumeto help instructors track exactly that. You can monitor checklist scores, spot patterns in learner performance, and break down which skills are consistently strong—or slipping.
Lumeto’s Artificial Clinical Evaluator (ACE) helps educators automate evaluations and customize assessments based on each learner’s needs and progress.
Key features of ACE include:
- Competency-Mapped Evaluations: Automatically assess learners using checklists tied to clinical objectives and learning goals.
- Real-Time AI Insights: Get instant feedback on learner decisions, communication, and performance during simulations.
- Customizable Scenarios & Metrics: Modify assessments and benchmarks to fit your institution’s specific training priorities.

In the example above, skills like CPR technique and defibrillation are being practiced, but there’s also a visible drop in session performance. That’s your signal to adjust content, tweak your teaching flow, or follow up with coaching.
Integration with Other Modalities
Virtual reality works best when it’s layered into your existing training strategy, not kept separate. Many programs are using it as a follow-up tool after live simulation. For example, a resident might run a difficult pediatric code in the sim center once, then revisit a similar scenario in VR weeks later to refresh their memory and sharpen their response.
VR also takes it further by removing the need to be on-site. Trainees can run pediatric cases remotely—on demand, from anywhere.
Challenges in Virtual Reality in Pediatric Care
As promising as VR is for pediatric training, there are real challenges that educators and institutions need to plan for:
Cost and Resource Requirements
VR is a more affordable alternative to full-scale sim labs. But there’s still an upfront investment. Programs need to budget for hardware, software, and technical support. Even a relatively simple setup can hit a snag if only one headset is available for dozens of students.
While VR doesn’t require a traditional lab, you still need a safe area for users to move freely without bumping into furniture or each other.
Lumeto helps reduce some of the friction. It runs on consumer-grade headsets like the Meta Oculus Quest 2 or 3, which can be purchased directly or bundled through Lumeto. The system supports both asynchronous and live (synchronous) training modules, giving instructors more flexibility.
On average, the initial IT setup takes about two hours per location—fast enough for most academic or hospital settings.
User Adaptation and Technical Difficulties
Adapting to virtual reality isn’t usually a major hurdle, but it does take a bit of orientation. In one nursing-focused VR study, students mentioned a few common issues—interface glitches or the occasional scenario bug.
What matters is how quickly users can get comfortable. Lumeto’s Train the Trainers program is built with that in mind. The comprehensive support model is designed to help both trainers and administrators feel confident during rollout. The platform includes interactive guides, product training materials, and built-in support to help users get up to speed.
A short intro session is usually all it takes to get new users comfortable enough to dive into clinical scenarios without hesitation.
Frequently Asked Questions About Pediatric VR
Is VR pediatric training suitable for all experience levels?
Absolutely. Simulations can be tailored to match the learner’s level. It can be used to train medical students, new nurses, or seasoned pediatric specialists looking to refresh rare-case management skills.
Do learners need prior gaming or tech experience to use pediatric VR?
No. Lumeto’s VR pediatrics training system is designed with an intuitive interface. After a brief orientation, even those with no gaming background can easily navigate clinical scenarios.
How is feedback delivered after a virtual reality session?
Feedback may be delivered automatically with our AI-powered artificial clinical evaluator or done manually by an instructor. Your instructors can review learner choices, timing, and communication patterns for coaching.
Is VR used to train for pediatric code blue situations?
Pediatric code simulations are among the most common and critical VR use cases. Learners practice recognizing early signs, leading the response, coordinating with teams, and adjusting care based on a child’s physiology.