
Scalable Training for Healthcare Teams in 2026 and Beyond
Global demand for care is surging while the supply of trained professionals struggles to keep up. The World Health Organization projects a shortfall of about 11 million health workers by 2030.
In the United States alone, forecasts warn of tens of thousands fewer physicians than needed by mid-decade. High burnout and turnover exacerbate the gap, with nearly 27.8% of healthcare staff departures linked to inadequate training opportunities.
Scalable training options for medical teams have become more important than ever. This article explores what scalable training means for healthcare, real-world examples, and the benefits it offers. We will also share some practical steps for hospitals and clinics to expand skill development in different areas.
What Is Scalable Training for Healthcare Teams?
Scalable training in healthcare refers to educational methods that can grow easily to accommodate large numbers of learners without sacrificing quality. Standardized content delivery and technology are used to reach many participants simultaneously or asynchronously.
The aim is not only to train more people, but to maintain consistent competencies and up-to-date knowledge across an expanding workforce.
Key characteristics of scalable training include:
- Flexibility: accessible anytime, anywhere via web or mobile
- Adaptability: content can be rapidly updated and pushed to all learners at once
- Efficiency: Educators can reach far more people with minimal incremental cost or effort compared to traditional training.
Instead of relying solely on limited classroom seats or trainer availability, a hospital might adopt virtual reality simulation modules. For example, hundreds of nurses could practice emergency response skills inside immersive scenarios on a VR platform like Lumeto. Everyone receives identical instructions, realistic feedback, and opportunities to repeat the procedure until they are confident.
Here’s how Lumeto helps clinicians learn, practice, and improve anytime:
Examples of Scalable Training for Healthcare Teams
Healthcare organizations globally are adopting a variety of scalable training models and tools. Below are some notable examples:
Virtual Simulation and VR Training
Simulation-based education is now scaling up through virtual reality (VR) and online simulations. VR training programs can immerse healthcare workers in realistic clinical scenarios using only a headset and software. Any number of learners can practice critical skills without needing a physical sim center.
Once the VR module is developed, it can be deployed across dozens of sites or thousands of users. Studies show VR-trained learners can make fewer errors in medical simulations compared to those trained by traditional methods.
AI enhancements are shaping the next stage of this training approach. For example, Lumeto has introduced the industry’s first conversational AI virtual patient that talks, moves, and reacts like a real person. It can show facial expressions, respond to commands, and adapt to each learner’s performance.
See the video below to watch how this works in a realistic clinical simulation:
Centralized E-Learning Platforms (LMS)
Many hospitals and clinics use Learning Management Systems to deliver training content online to all staff. An LMS centralizes courses, attendance, videos, assessments, and grading in one portal.
For instance, a nurse or pharmacist can complete required modules on new medication safety protocols via the LMS during breaks or after shifts, rather than attending off-site classes.
Thousands of employees can log in and learn simultaneously, with the system tracking their progress and compliance. As an example, the U.S. Veterans Health Administration’s online training network and many large health systems have used LMS platforms to push out COVID-19 safety training to tens of thousands of workers in a short time.
VR simulation modules can plug directly into the LMS as well. Trainees can launch immersive practice sessions from the same portal and repeat scenarios as often as needed.
Teachers and clinical educators often rely on an LMS to assign courses and monitor progress. Lumeto’s VR training platform supports that same structured approach, while adding realistic practice and live performance insights that help instructors guide learning more effectively.
Below is an example of a VR learning experience focused on evaluating a patient with a sudden, severe headache:
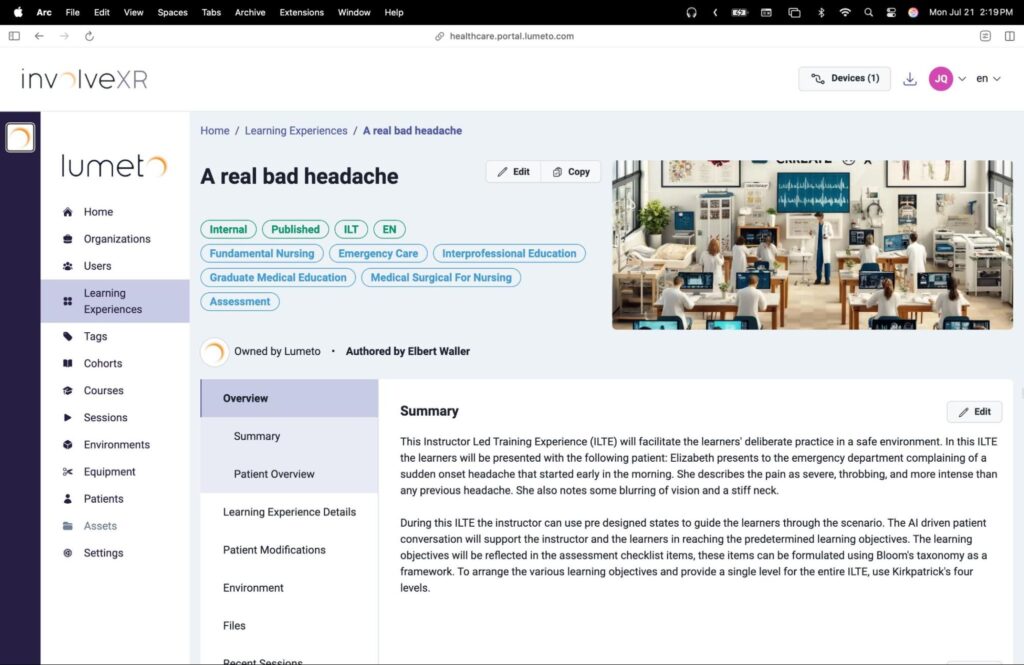
Mobile Microlearning
Mobile technology is another enabler of scalable training, particularly for frontline health workers in the field. In many low-resource settings, healthcare staff now receive training and updates via simple mobile phone applications or messaging. Examples include:
- SMS-based coaching for community health workers
- Short instructional videos for emergency care steps
- Quick quizzes and checklists for protocol refreshers
- Job-aid apps for medication guidance and triage decisions
Mobile learning is typically bite-sized and on-demand. A nurse at a remote clinic can review a 5-minute neonatal resuscitation module on her phone just before a shift, reinforcing knowledge at the point of need.
A strong example comes from Inova Health System, which rolled out “Leadership Moments,” a mobile microlearning program built for busy clinical teams. Short, 10-minute modules delivered directly to phones helped staff strengthen leadership skills during downtime.
Gamified and Interactive Online Courses
Another trend is the use of gamification and interactive learning to engage large numbers of health professionals. Many scalable e-learning programs now incorporate game elements (points, badges, leaderboards) to motivate learners to complete modules.
Gamified healthcare LMS solutions have shown significantly higher user engagement and knowledge retention compared to traditional methods.
Serious games and virtual escape-room style trainings have also been used to train clinicians on topics like infection control and sepsis recognition.
Key Benefits of Scalable Healthcare Education
Below are some key advantages of scaling up healthcare education:
Wider Reach and Equity of Training
Scalable education ensures that valuable knowledge reaches all corners of the health system. Digital platforms (VR + on-screen training systems) democratize training.
For example, rural hospitals can access the same high-quality procedural training as major medical centers. Here’s why this improves equity:
- Geography no longer limits learning: Rural clinics get the same clinical training as top teaching hospitals
- Shorter rollout times: Updated protocols can reach thousands of staff at once
- Reduced travel and cost barriers: No need for expensive trips to large training centers
- Inclusive of different schedules: Shift workers can learn during downtime or after hours
- Better access to rare-case practice: VR exposes clinicians to scenarios they may never see locally.
Cost-Effectiveness
One of the most touted benefits of scalable education is cost savings. Traditional training is expensive and scales linearly with headcount. In contrast, e-learning and digital simulations have high initial development costs, but then each additional learner is very low-cost.
At scale, the return on investment (ROI) is substantial; many organizations recoup initial platform costs within the first year through eliminated venue rentals, travel reimbursements, and productivity gains. Moreover, automation features cut administrative burden, freeing up educator time.
An analysis found that VR training becomes 52% more cost-effective than classroom training when training over 3,000 employees, due to savings on travel, instructor hours, and logistics.
Faster Onboarding
Scalable training methods can significantly speed up the training process for new hires and existing staff learning new skills. Digital courses and simulations are available on demand, enabling learners to progress at their own pace and often faster than scheduling multiple classroom sessions. Interactive tools also help people learn by doing, thereby shortening the time to competency.
Automated adaptive learning systems can quickly identify a learner’s strengths and weaknesses and focus training where needed, accelerating mastery.
Hospitals using Lumeto can monitor performance in real time. Below is an example of a VR assessment checklist that instantly shows which clinical actions were completed correctly:
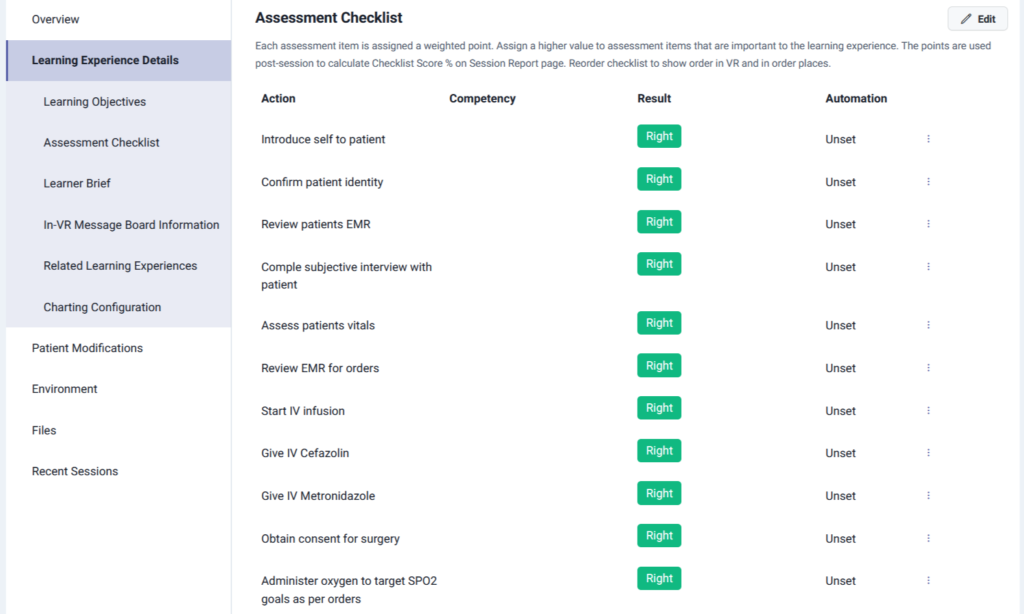
Enhanced Compliance
Keeping healthcare staff continuously trained at scale has direct benefits for compliance with standards and safety outcomes. Modern LMS platforms can automate and ensure completion of mandatory training.
Regular scalable training on infection control, medication safety, etc., helps embed safe practices across the organization, reducing errors and harm.
Simulation-Based Training in Healthcare
Simulation-based training deserves special focus as a critical component of scalable healthcare education. It involves recreating clinical scenarios so that practitioners can practice in a safe, controlled environment before treating real patients.
Historically, simulation in healthcare began with simple task trainers and static manikins used in nursing schools in the early 1900s. The field grew rapidly with Resusci-Anne (1960s) for CPR training, and later evolved into high-fidelity manikins capable of speech, pulses, and physiologic responses.
Modern technology has greatly expanded the scalability and impact of simulation training. Screen-based and VR simulations allow learners to experience scenarios on a computer or VR headset from anywhere. Because digital/virtual simulation does not require a full physical lab for every learner, it has strong potential to scale and reach dispersed or resource-limited settings.
Here’s some supporting evidence from research:
- A systematic meta-analysis of medical students reported a 22% absolute improvement in performance scores when trained with simulation compared to traditional methods.
- A review of health information system simulations found ≈90% of studies measured skill outcomes, and ≈55% showed significant improvement in learner performance.
- An in-situ simulation program for stroke care involving 650 patients reduced median door-to-needle time from 27 minutes to 13 minutes.
Digital simulation platforms like Lumeto also help instructors measure performance at scale. Instead of manually observing every learner, trainers can monitor objective results across large groups.
Lumeto’s Artificial Clinical Evaluator (ACE) tracks each action taken during a session and shows how skills improve over time. This means educators can quickly see who is ready for independent practice and who needs more coaching, without slowing down the training process.

How Hospitals and Clinics Can Scale Skill Development
Here are several actionable steps and considerations for hospitals and clinics looking to scale up skill development among their teams:
Blended Learning
Online modules can deliver consistent knowledge at speed, while short, focused sessions let learners apply skills hands-on. For example, a respiratory therapist might complete a quick module on ventilator alarms and decision-making at home, then join a brief lab session to handle the equipment in person.
Everyone arrives prepared, so precious classroom time is used for practical skill-building instead of lectures. Digital simulations also allow for repeated practice that would be difficult to squeeze into busy schedules using labs alone. During the COVID-19 pandemic, many institutions shifted to this blended model out of necessity.
Lumeto supports this blended model by allowing clinicians to practice realistic scenarios on laptops or in VR before attending an in-person session. Trainers get performance data in advance, so coaching during hands-on time is more targeted and effective.
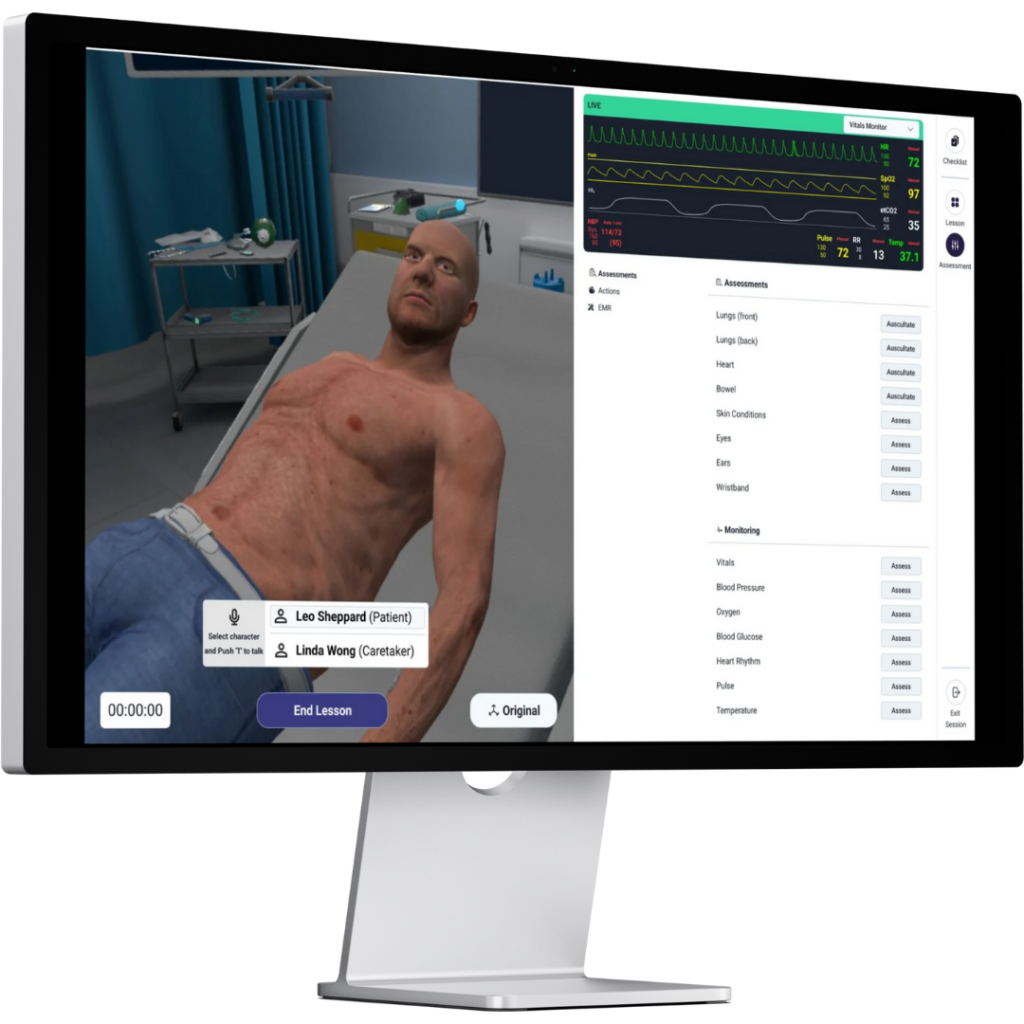
Flexible Scheduling
One key to engaging busy healthcare workers in training is to fit learning into their workflow. Long lectures or full-day classes pull staff off the floor and are hard to scale frequently. Instead, break training into short, focused microlearning modules that staff can complete in 10–15 minutes or less. Training should also work on any device a clinician has available.
Lumeto supports both synchronous (live) and asynchronous (on-your-own-time) learning in a simple process:
Here’s how it works:
- On-demand learning: Learners log in and complete VR or on-screen simulations anytime their schedule allows.
- Live instructor-led sessions: Educators can join sessions in real time, observe performance, and give instant coaching.
- Repeatable practice: Scenarios can be replayed as often as needed until skills are mastered.
- Data review: Performance reports are available to trainers and learners to track progress and guide feedback.
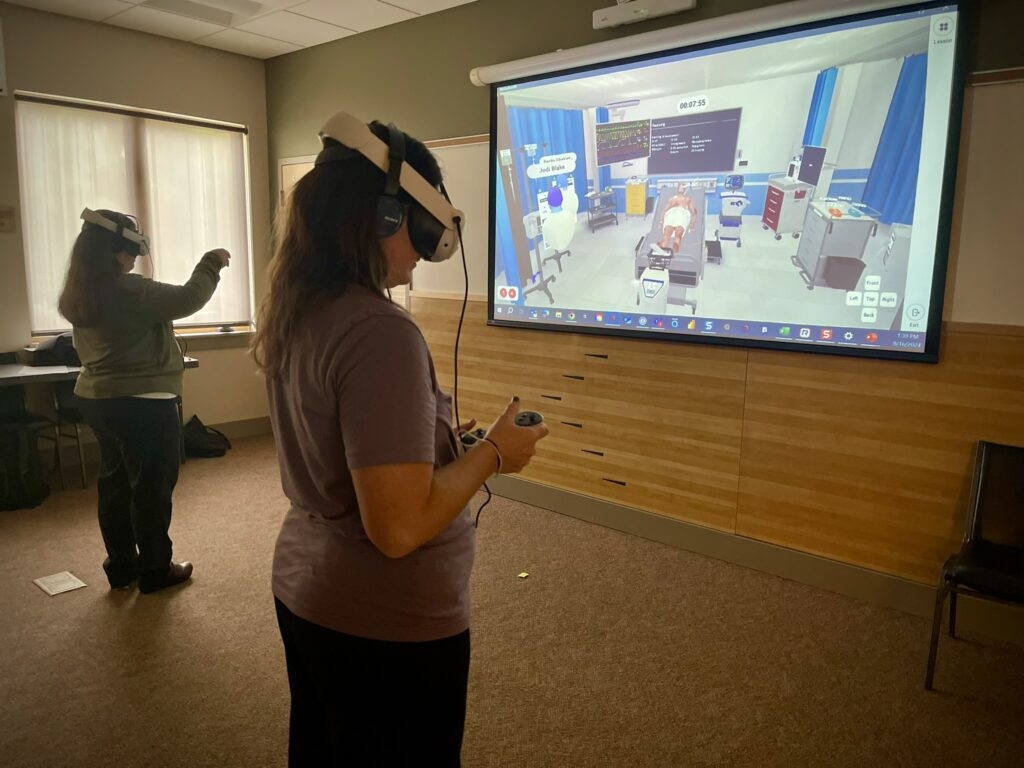

Training the Instructors
A strong human element remains essential when scaling practical skills. Rather than relying on one educator to train hundreds of staff, organizations can build capacity by developing local experts. Instead of having one educator train 500 nurses, you might train 25 trainers who each train 20 nurses in their unit.
When rolling out a new sepsis protocol, an education team might first train unit-based super-users who then deliver short workshops for their peers. This approach improves adoption because trainers understand their team’s workflows and challenges. It also enables ongoing coaching at the bedside, reinforcing new behaviors where they matter most.
Lumeto’s VR training platform offers a Train the Trainers Program that helps organizations grow internal simulation expertise quickly. The program equips educators and administrators to run sessions confidently and support staff directly on their units.
Here’s what the program includes:
- Three 1.5-hour sessions covering core platform skills and deployment
- Mock simulation sessions to build hands-on experience leading training
- Interactive resources to reinforce confidence and product knowledge
- Virtual delivery, so instructors in different locations can join together
Encourage Leadership Support
Hospital and clinic leaders should actively advocate for continuous training. Strategic and financial commitments are needed to truly expand simulation and other training broadly.
Leaders can show it by joining training sessions themselves and setting clear expectations for ongoing development. When clinicians see that training programs help them in their jobs (rather than distract from them), they become willing partners in expanding those programs.
Here are some practical leadership actions that help training scale:
- Allocate protected time and budget for learning
- Recognize and reward staff who complete training or build new skills
- Model participation by enrolling in the same learning modules as staff
- Set measurable goals for completion and competency improvement
- Include training progress and quality in organizational reporting
- Highlight wins (e.g., full staff completion of a new protocol)
- Gather frontline feedback to keep training relevant and useful
Measure Impact
Use data to monitor how your scaling efforts are performing and where to adjust. For example, if after a big sepsis training push you see an increase in early sepsis recognition and reduced ICU transfers, that’s an outcome to report and build on.
Track metrics like:
- Training completion rates
- Assessment scores
- Clinical performance indicators
- Learner confidence ratings before and after training
Some advanced programs use predictive analytics to anticipate skill gaps and recommend training before an issue arises.
Have a quick survey after each course or simulation asking how useful it was and suggestions. Use all this input to refine the training content, modalities, and frequency.
FAQs About Scalable Healthcare Education
What makes a training program “scalable” in the first place?
It must deliver the same high-quality experience to large numbers of learners, without major increases in cost, staff time, or physical space requirements.
How quickly can training scale across multiple locations?
Once digital modules are built, they can be deployed instantly to thousands of staff, even across different campuses and regions.
How can training scale without overwhelming educators?
Digital and simulation-based systems allow instructors to reach far more learners at once. Automated scoring and feedback reduce manual oversight, so educators focus on coaching where it’s most needed.